Figure 4.
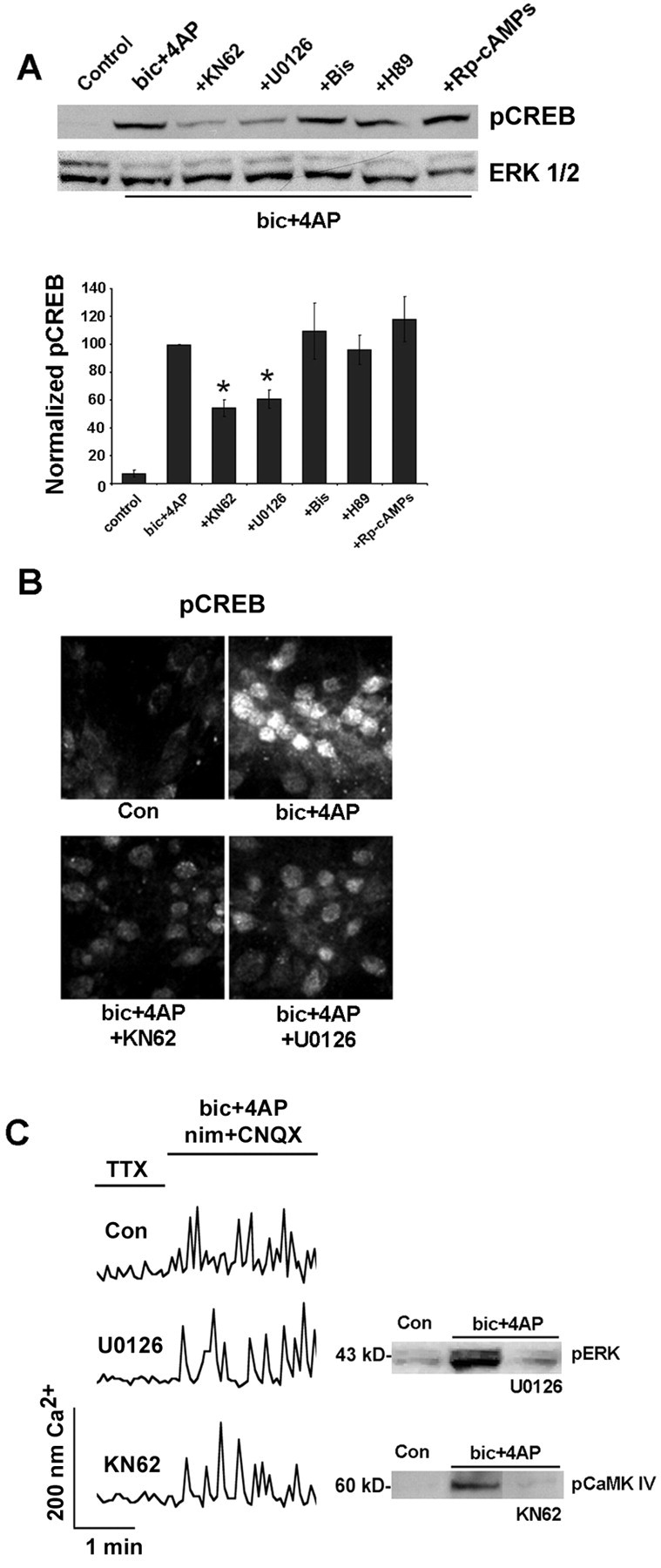
The MAPK and CaMK pathways couple synaptically evoked NMDA receptor activation to CREB phosphorylation. A, Initially, cortical cultures were pretreated (for 30 min) with U0126 (10 μm), KN62 (10 μm), H89 (5 μm), Rp-cAMPs (300 μm), or bisindolylmaleimide (Bis; 1 μm). Then NMDA receptor-mediated synaptic activity was elicited (10 min) by bicuculline (bic) plus 4-AP in the presence of nimodipine and CNQX. Both U0126 and KN62 attenuated CREB phosphorylation. Mean densitometric band analysis is shown in the bars below. Data are representative of triplicate determinations. *Significant difference (p < 0.05) relative to the bicuculline plus 4-AP condition. Intensity values were normalized to the bicuculline plus 4-AP treatment condition, which was set equal to 100%. Data are representative of triplicate determinations. B, Immunofluorescent staining for pCREB was used to compliment the Western blot analysis. Relative to control cultures, the administration of bicuculline increased pCREB expression; pretreatment with KN62 or U0126 attenuated the synaptic activity-dependent increase in CREB phosphorylation. C, To determine whether inhibition of MAPK and CaMK signaling disrupts Ca2+ response characteristics, we loaded cortical cultures with fura-2, pretreated them (10 min) with 10 μm KN6 or 10 μm U0126, and examined the capacity of NMDA receptor-mediated synaptic activity to stimulate Ca2+ transients. Representative examples show that robust Ca2+ transients were generated in the presence of these inhibitors. As an additional control, Western blot analysis was used to examine the potency of these inhibitors. U0126 (10 μm) attenuated synaptically evoked ERK phosphorylation; KN62 (10 μm) attenuated synaptically evoked CaMKIV phosphorylation. Con, Control.
