Figure 7.
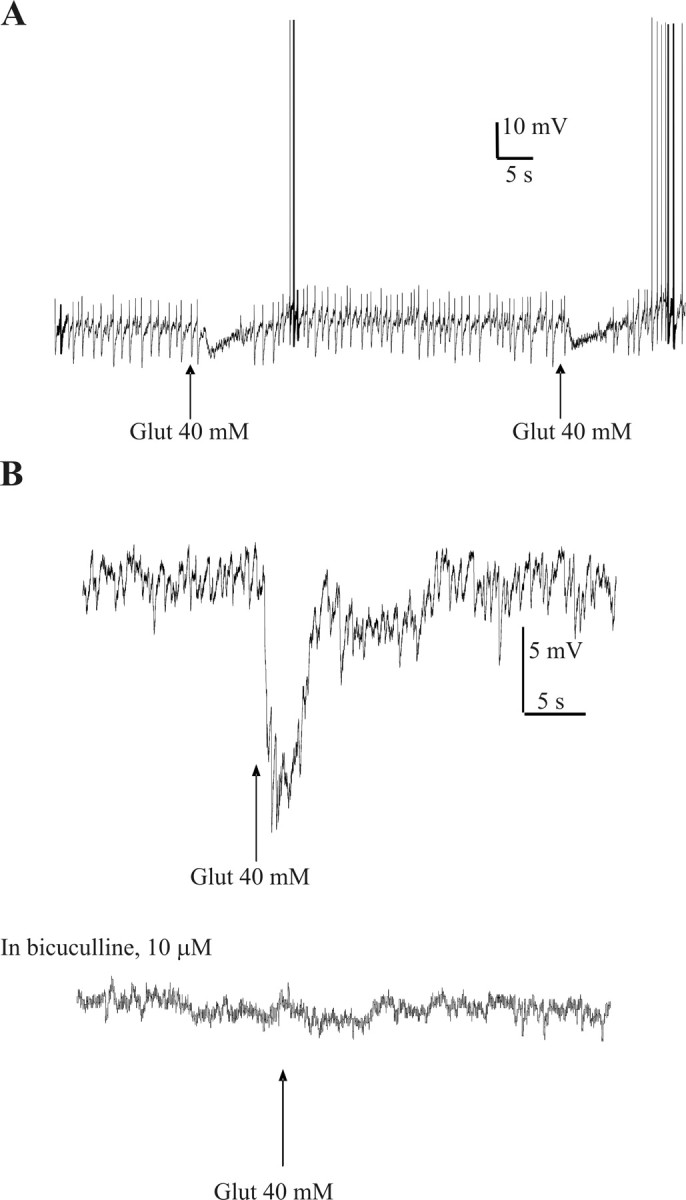
Glutamate microinjections in the CAA hyperpolarize SPNs, and these effects are antagonized by bicuculline. A, Repeated microinjections of glutamate into the CAA caused reproducible hyperpolarizations in SPNs in the IML. In this cell, spikelets were also observed that are likely to be attributable to action potentials in an electrically coupled SPN. These spikelets were also reduced during glutamate application; this effect is not solely attributable to hyperpolarizing the membrane, because manual hyperpolarization to this level was not sufficient to reduce the frequency of spikelets in this cell. This indicated that the coupled SPN was also inhibited by glutamate microinjection. B, Glutamate microinjection in the CAA hyperpolarized this SPN in the IML. Bicuculline (10 μm) antagonized this hyperpolarization.
