Figure 6.
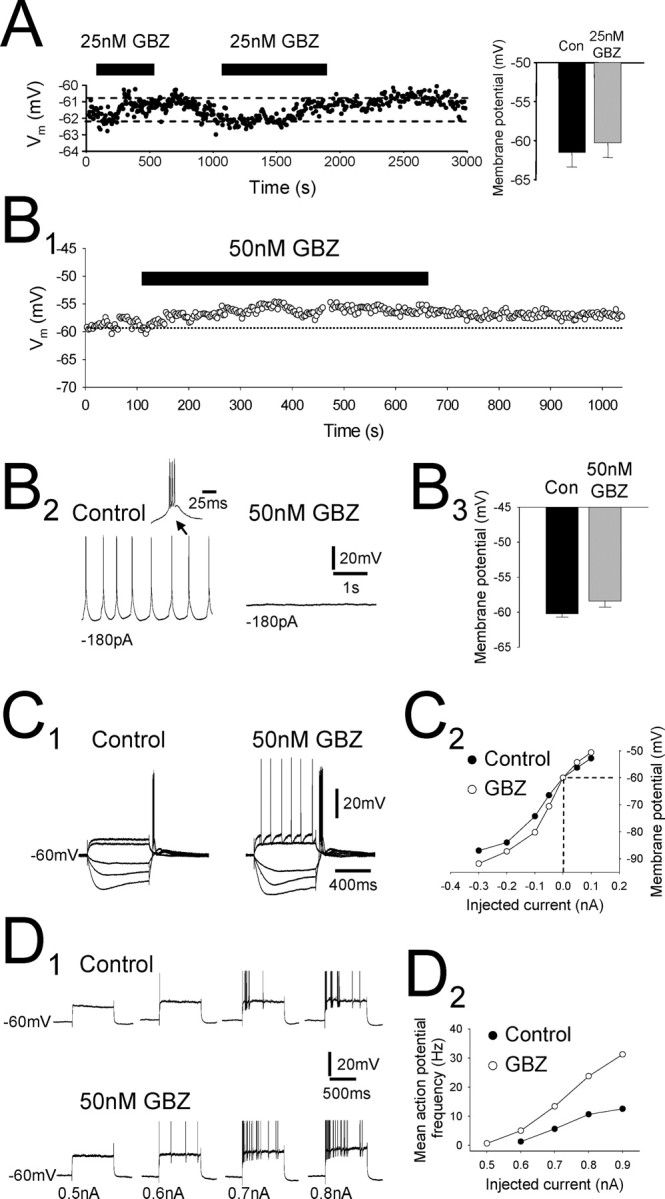
Preferential block of the tonic current modulates the membrane properties and firing of individual TC neurons. A, Intracellular current-clamp recording from a dLGN TC neuron consisting of the membrane potential sampled every 3 s. Injected holding current was constant throughout the experiment. Bath application of 25 nm GBZ (black bars) causes a small (∼1 mV) depolarization of the membrane potential that could be reversed during wash. Bar graph to the right shows membrane potential before (black column) and after (gray column) 25 nm GBZ application for all recorded neurons. B1, In another dLGN TC neuron, application of 50 nm GBZ caused a larger depolarization (∼3 mV) in membrane potential. B2, In the same neuron, low-threshold repetitive burst firing (left) was apparent under control conditions but was blocked after the bath application of 50 nm GBZ (right). Inset is one of the low-threshold bursts. B3, Graph showing the membrane potential of TC neurons before (black column) and after (gray column) 50 nm GBZ application for all recorded neurons. C1, Response of a dLGN TC neuron to depolarizing (100 and 200 pA) and hyperpolarizing (–50, –100, and –200 pA) current steps both before (left) and after (right) bath application of 50 nm GBZ. Note the appearance of action potentials on the largest depolarizing current step after GBZ application. C2, Current–voltage plot for the neuron in C1. Values were taken from the maximum deflection of the membrane potential during the current steps. GBZ application causes an increase in apparent input resistance in response to hyperpolarizing current steps. D1, Response of a dLGN TC neuron to depolarizing current steps of increasing magnitude (top). Bath application of 50 nm GBZ increased the number of action potentials observed in response to almost all of the current steps (bottom). D2, Plot of mean action potential frequency against current step amplitude for the same cell as in D1. GBZ application caused a large increase in the frequency of action potentials, especially for the largest current steps. In D, action potentials have been truncated for clarity.
