Figure 5.
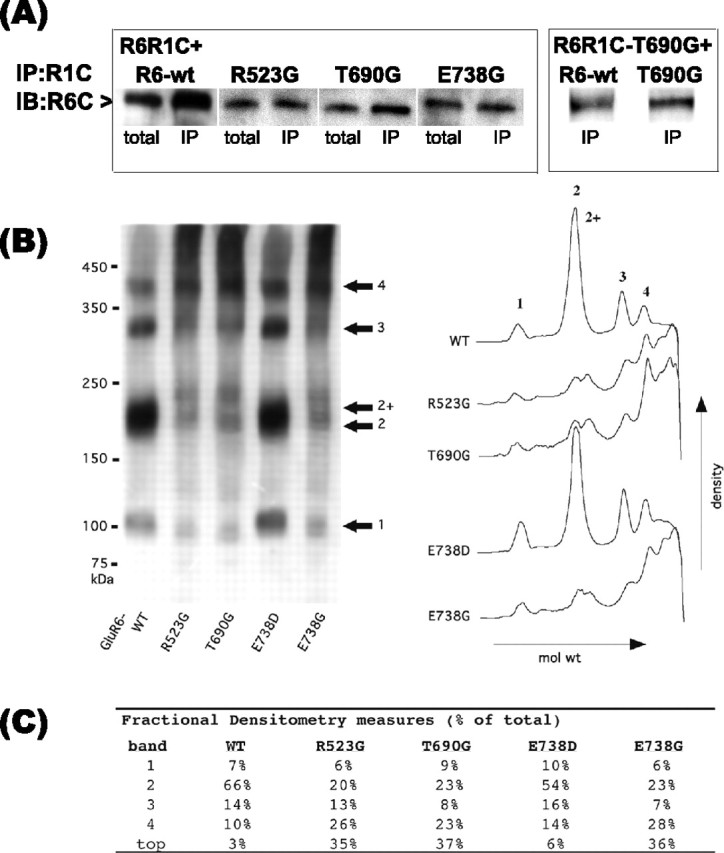
GluR6-binding site mutant oligomerization. A, Solubilized protein (50 μg) from cotransfection of R6R1C with GluR6-wt, R523G, T690G, or E738G (1:1) or R6R1C-T690G with GluR6-wt or T690G was immunoprecipitated (IP) with rabbit C-GluR1 antibodies (left). Washed precipitates subjected to Western blot analysis with C-GluR6 antibodies demonstrate that the GluR6-binding site mutants and GluR6-wt oligomerize with R6R1C. Control immunoprecipitates of R6R1C and GluR6-wt transfected alone were negative. The blot is representative of duplicate experiments. IB, Immunoblot. B, Native-PAGE densitometric analysis. Total cell proteins solubilized with 1% Triton X-100 were separated by PAGE on 3-7.5% Tris-glycine gradient gels under nonreducing conditions. C-GluR6-immunoreactive proteins segregated to four prominent bands having approximate molecular masses of 100, 200, 300, and 400 kDa, consistent with GluR6 monomers, dimers, trimers, and tetramers. B, C, Densitometric analysis indicating relative amounts of immunoreactive proteins of varying molecular weight. Relative intensity differences might reflect either a greater prevalence of large nonfunctional mutant receptor complexes (R523G, T690G and E738G) or indicate that the mutant receptor complexes are more stable than their functional counterparts. Relative band intensities are given combining the two putative dimeric forms.
