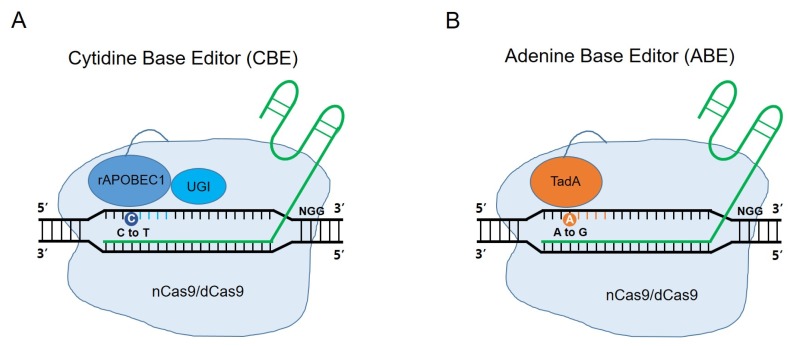
Fig. 2.
Schematics of base editors (BEs). (A) The cytidine base editor (CBE) consists of cytidine deaminase rAPOBEC1 (blue), uracil glycosylase inhibitor (UGI) and nickase Cas9 (nCas9) or dead Cas9 (dCas9). CBE can induce targeted nucleotide substitutions, such as C to T, or G to A conversion. (B) The adenine base editor (ABE) consists of adenine deaminase TadA (orange,) and nCas9 or dCas9. ABE can induce targeted nucleotide substitutions, such as A to G, or T to C conversion. The active window of CBE and ABE is 4–8 nucleotides, in the distal region of the guide RNA.