Fig. 4. Structure and dynamics of TtClpP from x-ray crystallography, MAS NMR, and MD simulations.
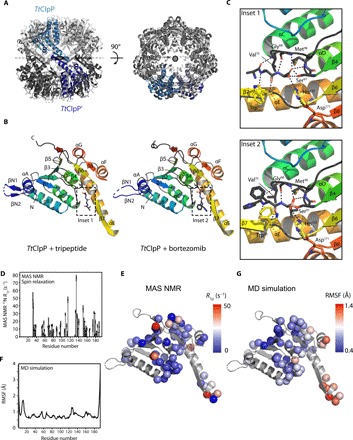
(A) Side and top views of the TtClpP 14-mer. One TtClpP monomer per heptameric ring (light and dark gray) is highlighted in light and dark blue, respectively. (B) Cartoon representation of the TtClpP monomer in peptide-bound (left) and bortezomib-bound (right) states. Helices are named by letters, and strands are indicated by numbers. A zoom of the ligands present in the active sites (dashed boxes) is shown in (C). (C) Substrate-binding pocket of TtClpP. The residues involved in the binding to the model peptide (inset 1) and bortezomib (inset 2) are shown as sticks. (D and E) Residue-wise MAS NMR amide 15N R1α relaxation rate constants. High R1α rate constants point to enhanced nanosecond-to-millisecond motions and are found primarily in loop regions and in helix αE, as shown in (C). (F and G) MD-derived root mean square fluctuations (RMSFs) over the 1-μs-long MD trajectory of the assembled 14-mer ClpP.
