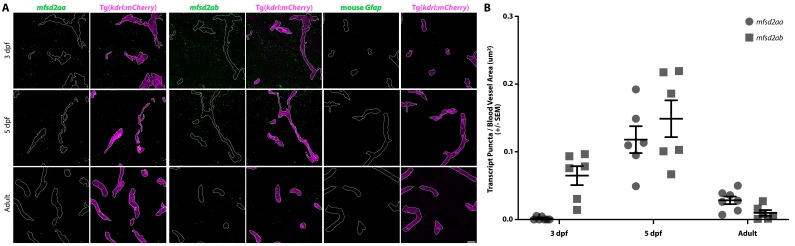
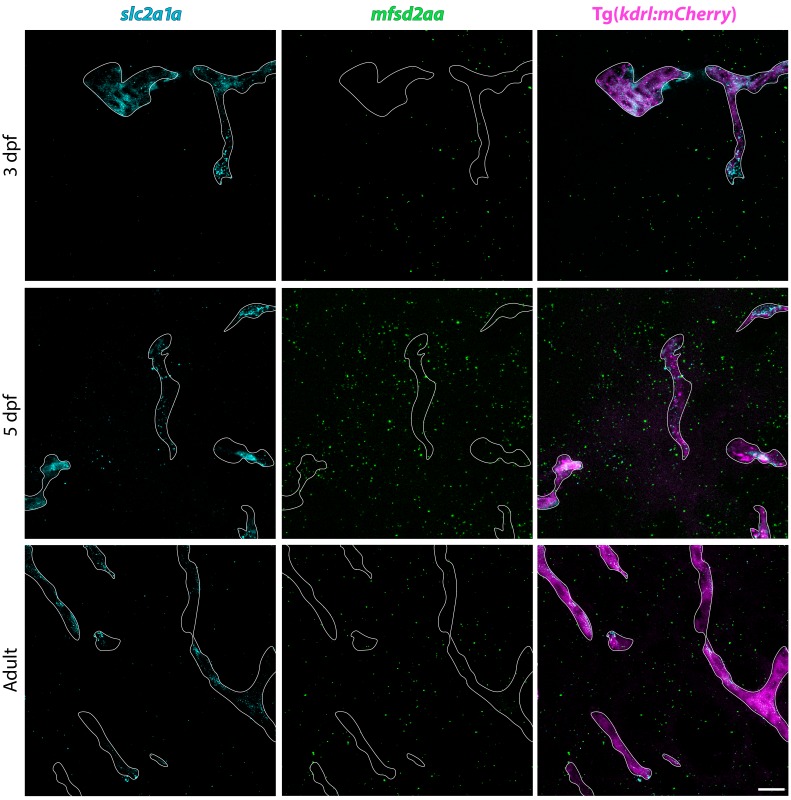
Figure 4. Fluorescent in situ hybridization (FISH) reveals vascular signal for both mfsd2aa and mfsd2ab at 5 dpf.
(A) FISH for mfsd2aa (left), mfsd2ab (middle) and mouse Gfap negative control (right) in Tg(kdrl:mCherry) 3 dpf, 5 dpf and adult brain tissue. FISH for mfsd2aa (left) reveals no vascular expression above background at 3 dpf, high levels at 5 dpf and low levels in adult blood vessels. FISH for mfsd2ab (middle) reveals high levels of vascular signal at 3 and 5 dpf and negligible vascular signal in adults. Neither Mfsd2a paralogue was expressed exclusively in the vasculature, outlined in white, at any time examined and mfsd2ab displayed higher overall expression throughout the larval brain than mfsd2aa. Scale bar represents 10 µm. (B) Quantification of the number of transcript puncta per blood vessel area in 3 dpf, 5 dpf and adult brain sections after background (mouse Gfap expression) subtraction. N = 6 sections from at least 3 different fish.