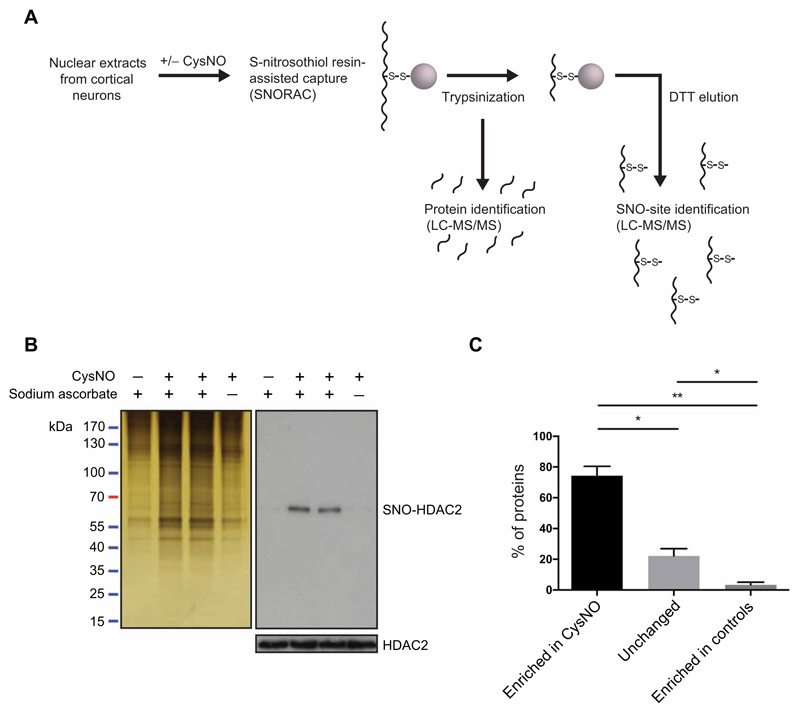
Fig. 1. Identification of S-nitrosylated nuclear proteins using SNORAC.
(A) Nuclear extracts from E17 cortical neurons were treated with CysNO and SNO-Ps captured using SNORAC. Resin-bound proteins were trypsinized, and eluted fragments were analyzed by quantitative MS to identify the proteins enriched in CysNO-treated groups. A second elution step was carried out using dithiothreitol (DTT) to release fragments containing the previously S-nitrosylated cysteines and to identify S-nitrosylation sites (SNO sites). (B) Silver stain of proteins isolated using SNORAC and HDAC2 Western blotting on SNORAC eluates and total inputs. Sodium ascorbate is required for isolation of SNO-Ps using SNORAC. Blots are representative of five independent experiments. (C) Average percentage of proteins detected by MS as enriched in CysNO (≥2-fold versus control), unchanged (<2-fold, >0.5-fold; CysNO versus control), or enriched in controls (≤0.5-fold; CysNO versus control). Control groups constitute Cys only and CysNO without ascorbate. Data are means ± SEM from five independent experiments. *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01 by row means one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) and Tukey post hoc test.