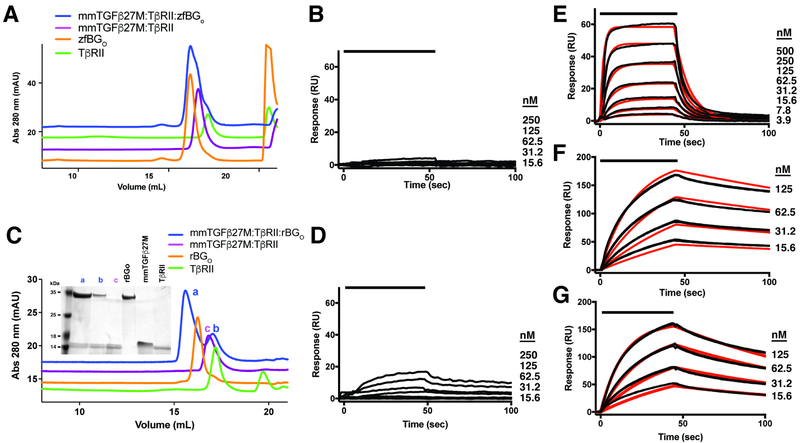
Figure 5. Binding of monomeric TGF-β by BGO.
A,C. SEC chromatograms to assess binding of zfBGO (A) or rBGO (C) to the mmTGF-β2-7M:TβRII binary complex. Chromatograms of the mmTGF-β2-7M:TβRII:BGO ternary complex, the mmTGF-β2-7M:TβRII binary complex, TβRII, and BGO are shown in blue, magenta, green, and orange, respectively. Shown in the inset in panel C is a non-reducing SDS-PAGE gel of the major peaks that eluted. B, D. SPR sensorgrams for binding of zfBGO (B) or rBGO to immobilized mmTGF-β2-7M. E. SPR sensorgrams for binding of TβRII to mmTGF-β2-7M. Kinetic fit is shown in red over the experimental data shown in black. F-G. SPR sensorgrams for binding of zfBGO (F) or rBGO (G) to immobilized TGF-β2. Kinetic fit is shown in red over the experimental data shown in black. SPR experiments shown in panels B, D, and E were performed using the same neutravidin-coupled CM5 sensor chip with captured biotinylated avi-mmTGF-β2-7M. See also Figure S9.