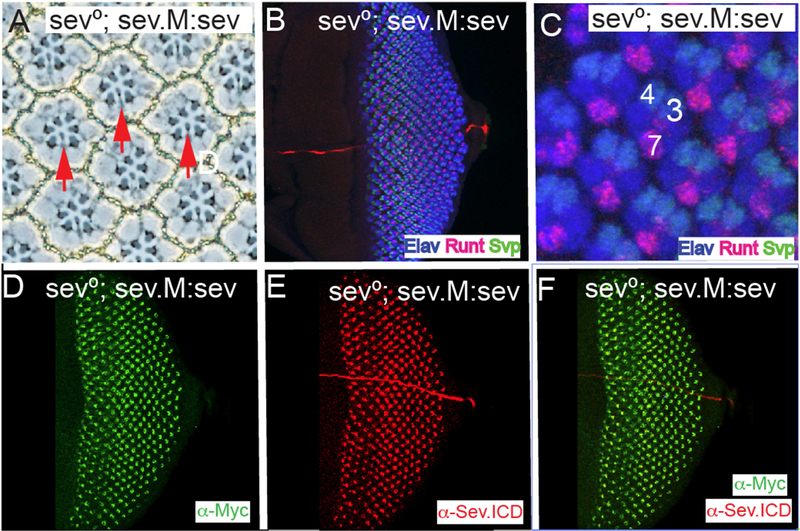
Figure 5. A heterologous signal sequence substitutes for the Sev N-terminal hydrophobic domain.
All panels show images from sev°; sev.M:sev animals in which the N-terminal hydrophobic domain and all residues N-terminal to it are replaced with a conventional signal peptide followed by the Myc tag. (A) In adult eyes all R7s are rescued (red arrows). (B–F) Eye discs stainings. (B, C) show that pattern formation is normal as monitored by Elav, Runt and Svp expressions, and R7s are specified at the correct time and position. (D) α-Myc staining highlights the normal Sev expression pattern. (E) α-Sev.ICD shows the normal Sev expression pattern. (F) Superimposition of the Myc and Sev staining show their coincident expression in the Sev expressing cells.