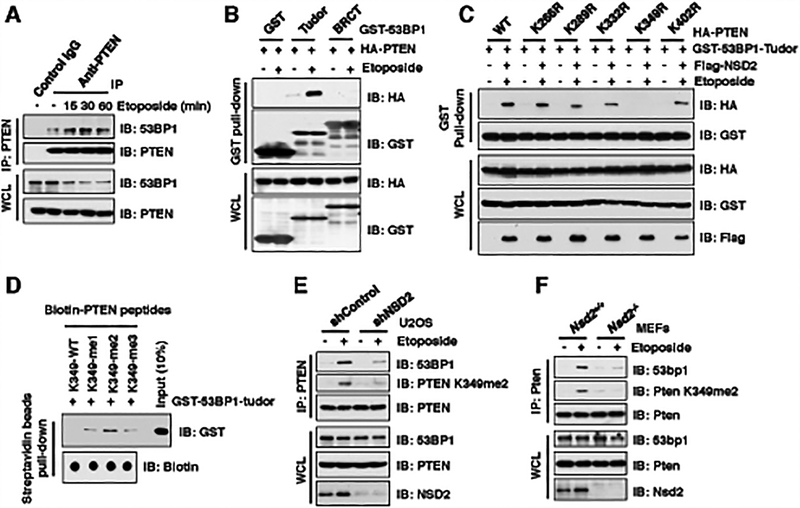
Figure 3. NSD2-mediated di-methylation of PTEN is recognized by the tudor domain of 53BP1.
(A) Etoposide treatment enhanced PTEN interaction with 53BP1. IB analysis of anti-PTEN IPs and WCL derived from U2OS cells treated with 30 μM etoposide as indicated time points before harvesting.
(B and C) PTEN-K349R mutant disrupted its binding with 53BP1 upon etoposide treatment. IB analysis of GST pull-down and WCL derived from U2OS cells transfected with the indicated constructs. 36 h after transfection, cells were treated with/without 30 μM etoposide for 30 min and harvested for GST pull-down assays.
(D) 53BP1 tudor domain had a high affinity with K349-me2-PTEN peptides. 1 μg of indicated biotin-labeled synthetic PTEN peptides were incubated with 250 ng purified recombinant GST-tagged 53BP1 tudor domain, respectively. Streptavidin beads were added to perform pull-down assays and precipitations were analyzed by IB. Dot blot assays were performed to show equal amount of biotinylated peptides was used for the pull-down assay.
(E and F) Depletion of NSD2 disrupted PTEN interaction with 53BP1. IB analysis of anti-PTEN IPs and WCL derived from U2OS cells stably expressing shNSD2 (E) or Nsd2−/− MEFs (F) that were treated with/without 30 μM etoposide for 30 min before harvesting.