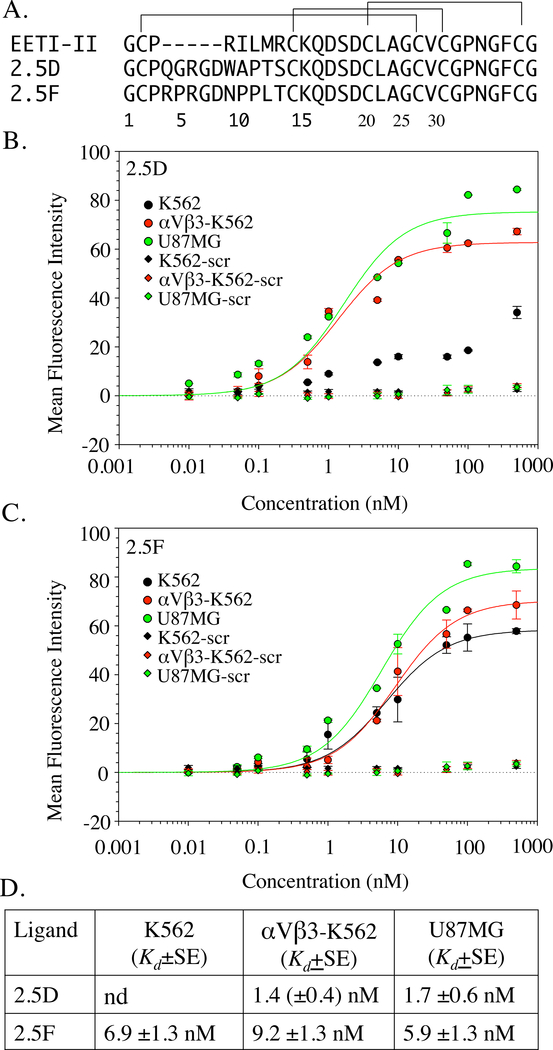
Figure 1. Primary sequence and binding properties of knottins 2.5D and 2.5F.
(A) The primary structure of EETI-II and of the engineered knottins 2.5D and 2.5F, where the 6-residue trypsin-binding sequence (P3RILMR) in native knottin is replaced with an 11-residue sequence containing the RGD motif. (B, C) Dose-response curves showing binding of Fc fusions of 2.5D (B), 2.5F (C) or a scrambled (scr) knottin (B, C) to native integrins expressed on U87MG, αVβ3 expressed on transfected K562 cells (αVβ3-K562), and native α5β1 on K562 cells. Points display the mean and standard deviation for triplicate determinations. (D) Equilibrium binding constant (Kd) values from the binding data shown in B, C, along with the standard error derived from the fitted curves. The Kd value derived from the curve fit of 2.5D-Fc binding to K562 in Figure 1B is not reliable as determined by the P value for the parameter, and thus not reported in Fig.1D. nd, not determined.