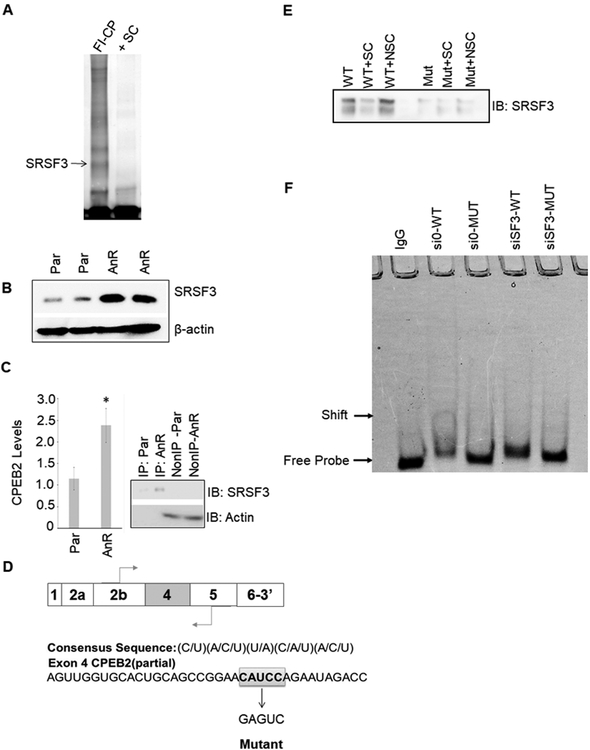
Figure 1: SRSF3/SRp20 binds specifically to exon 4 in the CPEB2 pre-mRNA.
A. MDA-MB-231 nuclear extract was incubated with either FITC-conjugated CPEB2 exon 4 sequence + “cold” nonspecific competitor (FI-CP) or pre-incubated with 100X “cold” CPEB2ex4 as a specific competitor (+SC). Samples were then electrophoresed and bound proteins were extracted and subjected to proteomic analysis. B. Lysates of Parental (Par) and anoikis resistant (AnR) MDA-MB-231 cells were immunoblotted and probed for the indicated antibodies. C. SRSF3-specific antibody was used for CLIP-qRT-PCR to detect CPEB2 levels in either MDA-MB-231 parental or AnR cells. Real-time PCR to CPEB2 at exon 4 was evaluated (data represented as n = 3 ± standard deviation (sd), * = p < 0.05). IP=immunoprecipitated fraction. Non-IP=Non-IP’d fraction. D. The consensus sequence for SRSF3 and a partial sequence of exon 4 highlighting the proposed SRSF3 binding site. E. SBAP assay was used to detect SRSF3 bound to exon 4 of CPEB2. Recombinant SRSF3 was incubated with biotinylated CPEB2 exon 4 RNA oligos with WT or mutant SRSF3 ESE cis-element. Samples were incubated with either biotin labeled CPEB2 exon 4 sequence + “cold” nonspecific competitor (NSC) or pre-incubated with 100X “cold” unlabeled CPEB2ex4 as a specific competitor (+SC). F. EMSA analysis of siRNA-depleted expression of SRSF3 in MDA-MB-231 cells. EMSA labels correspond to MDA-MB-231 cells treated with siRNA control and then total protein lysates incubated with wild type CPEB2 exon 4 ESE RNA (si0-WT), siRNA control treated cell lysates incubated with mutant CPEB2 exon 4 ESE RNA (si0-MUT), siRNA to SRSF3 treated cell lysates incubated with wild type CPEB2 exon 4 ESE RNA (siSF3-WT), or siRNA to SRSF3 treated cell lysates incubated with mutant CPEB2 exon 4 ESE RNA (siSF3-MUT). Sequences are indicated in the Materials and Methods section. Control samples were incubated with nonspecific IgG.