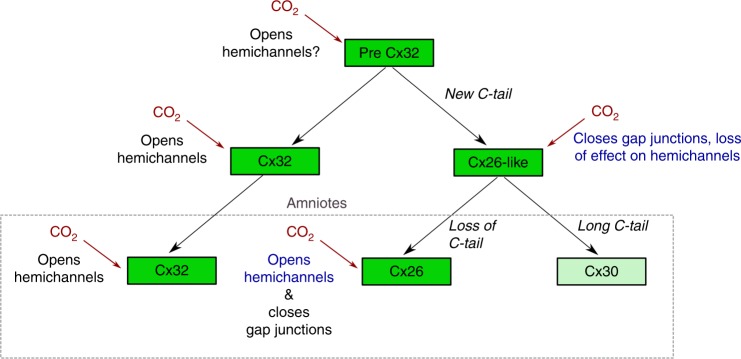
Fig. 10.
Inferred evolution of CO2-dependent functionality in the Cx32 and Cx26-like clades. The common ancestor of the Cx32 and Cx26-like genes (Pre Cx32) most likely had the carbamylation motif (CM). We postulate that this was originally used to regulate the opening of hemichannels; the CM and this functionality has been preserved in Cx32 to the present day. The emergence of the Cx26-like gene was accompanied by a de novo function for the CM — gain of CO2-dependent gap junction closure, but at the cost of losing CO2-dependent hemichannel opening. In the pre-amniote world, the functions of opening hemichannels and closing of gap junctions were subserved by different gene products. With the evolution of amniotes, the Cx26-like gene was duplicated to give Cx26 and Cx30. Cx30 gained a long C-terminal tail and in many cases lost the carbamylation motif. Cx26 in amniotes lost the C-terminal tail and regained the ability of CO2 to open the hemichannel. (Green box indicates near-universal presence of carbamylation motif, light green box presence of carbamylation motif in some species but not others)