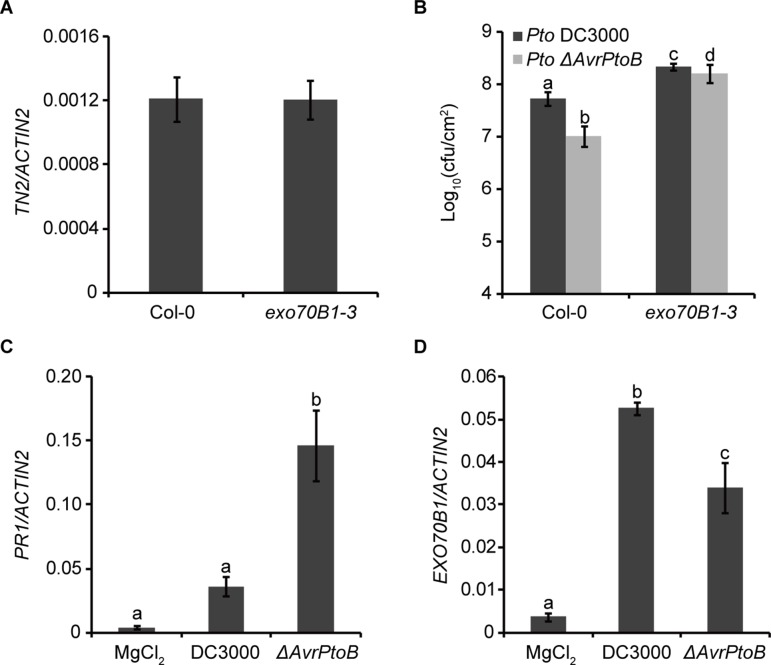
Figure 6.
AvrPtoB overcomes EXO70B1-mediated resistance. (A) TN2 transcript levels were examined by RT-qPCR. Total RNA was isolated from the indicated 10-day-old seedlings. The mRNA expression level was normalized to the reference gene ACTIN2. Data represent the mean and standard deviation of three biological replicates. Three technical replicates for each biological sample were used. This experiment was repeated three times with similar results. (B) AvrPtoB contributes to the virulence of Pto DC3000, which is dependent on its ability to disable the function of EXO70B1. Ten-day-old Col-0 and exo70B1-3 seedlings were infected with Pto DC3000 and Pto ΔAvrPtoB. The bacterial growth assays were performed 3 days after infection. Results represent the mean and standard deviation of three independent experiments each consisting four independent biological samples. cfu, colony-forming units. The lowercase letters indicate statistically significant differences (P < 0.05; nested ANOVA). (C) and (D) Pto DC3000 enhances the expression of EXO70B1. Leaves of soil-grown wild-type Col-0 Arabidopsis plants were hand infiltrated with Pto DC3000 or the Pto ΔAvrPtoB mutant at 108 cfu/ml and harvested at 24-h postinoculation. The transcript levels of PR1 and EXO70B1 were measured by RT-qPCR as described above. Data represent the mean and standard deviation of three biological replicates. Three technical replicates for each biological sample were used. These experiments were repeated three times with similar results. The lowercase letters indicate statistically significant differences (P < 0.05; one-way ANOVA).