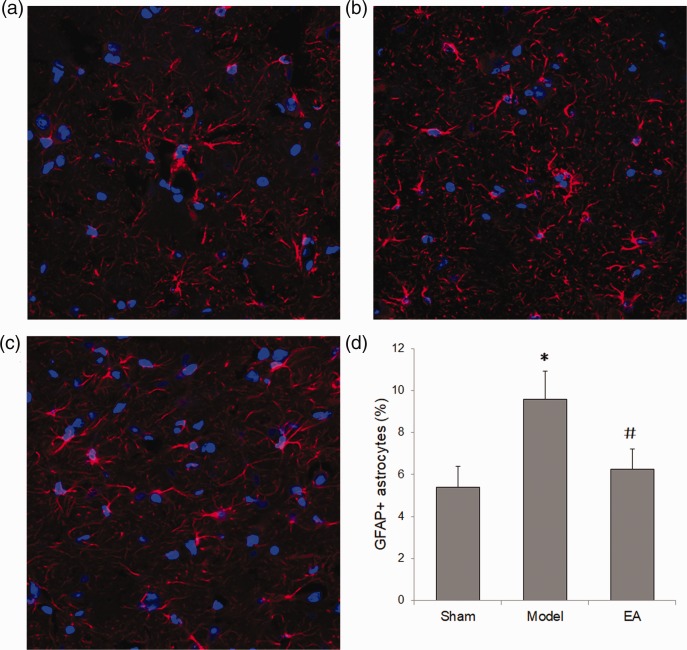
Figure 2.
Electroacupuncture (EA) reduced the astrocyte number in the hippocampus of rats with postoperative cognitive dysfunction (POCD). Rats were sacrificed on day 1 following surgery to obtain hippocampal tissue for immunofluorescence staining with anti-glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) antibody. Representative photomicrographs show GFAP-positive astrocytes and DAPI-stained nuclei (n = 8 per group): (a) Sham group; (b) POCD Model group; and (c) electroacupuncture group; (d) summary data showing that electroacupuncture treatment significantly attenuated the increased GFAP-positive astrocytes seen in the hippocampus of rats with POCD. Data presented as mean ± SD; *P < 0.05 versus sham group; #P < 0.05 versus model group (one-way analysis of variance); original magnification × 200.