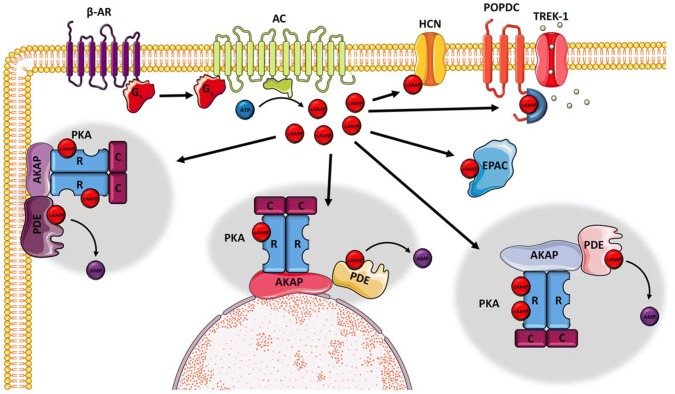
Fig. 1.
The cAMP signalling pathway. Activation of adenylyl cyclase (AC) by G-coupled receptors (GPCR) via Gs leads to an accumulation of cAMP, which is bound by a number of different cAMP effector proteins, namely HCN channels and POPDC proteins, which are both membrane-bound, while EPAC and PKA are cytoplasmic proteins. PKA is bound by a diverse group of anchor proteins (AKAP), which also recruit PDE isoforms forming a nanodomain. PKA activation and substrate phosphorylation is under tight spatiotemporal control. There are a large number of AKAP proteins in cells creating many different cAMP nanodomains in different subcellular compartments (grey halo). AKAP proteins also bind other signalling molecules forming a platform also allowing cross-talk between signalling pathways