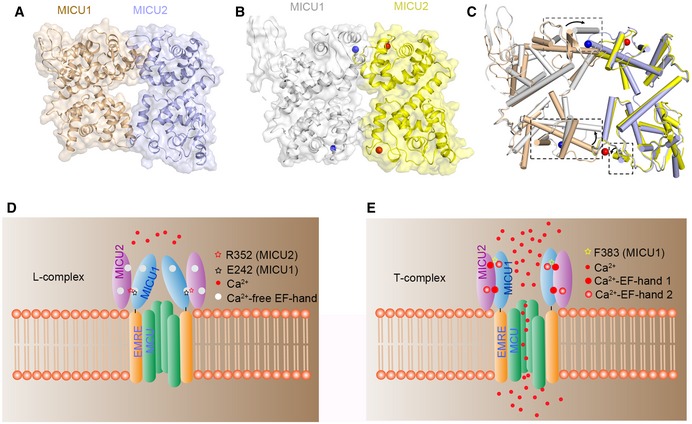
Figure 5. Working model of the MICU1–MICU2 heterodimer and the regulation of Ca2+ uptake.
-
A, BSpace filling and cartoon representation of heterodimer structures in the Ca2+‐free (A) and Ca2+‐bound states (B). Both structures are built based on the MICU1 homodimer structure (PDB code: 4NSC) in the apo state. Ca2+‐free and Ca2+‐bound MICU1 were colored in wheat and gray, respectively. Ca2+‐free and Ca2+‐bound MICU2 were colored in purple and yellow, respectively. Calcium ions are shown as blue and red spheres in MICU1 and MICU2, respectively.
-
CComparison of MICU1–MICU2 structures in the apo (wheat and purple) and Ca2+‐bound states (gray and yellow). The conformational differences are highlighted by boxes (black dotted lines). The black arrows show the direction of the conformational change from apo to Ca2+‐bound state.
-
D, EProposed model for mitochondrial Ca2+ uptake regulated by MICU1–MICU2. In the apo state, MICU1–MICU2 form a loose complex which inhibits the uniporter. Upon Ca2+ binding, the conformational changes of the EF‐hands promote a transition to a more compact state, which activates Ca2+ uptake.
