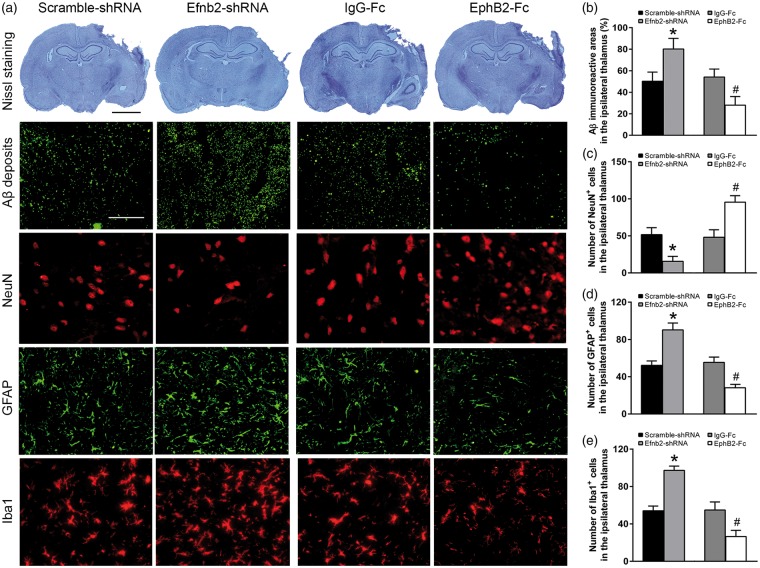
Figure 6.
EphrinB2 activation and Aβ deposits as well as secondary thalamic damage after cortical infarction. (a) Nissl staining showing cerebral infarction and immunostaining for Aβ, NeuN, GFAP and Iba1 in the ipsilateral thalamus of the Scramble-shRNA, Efnb2-shRNA, IgG-Fc and EphB2-Fc groups at seven days after MCAO. Efnb2-shRNA treatment markedly increased Aβ loads, the number of GFAP+ and Iba1+ cells, while decreased the number of NeuN+ cells. In contrast, EphB2-Fc infusion decreased Aβ loads, the number of GFAP+ and Iba1+ cells, whereas increased the number of NeuN+ cells. Scale bar: 2 mm and 50 µm. (b–e) Quantitative analysis of Aβ loads, the number of NeuN+, GFAP+ and Iba1+ cells. n = 8, data are expressed as median ± interquartile range. *P < 0.05 compared with the Scramble-shRNA group, #P < 0.05 compared with the IgG-Fc group.