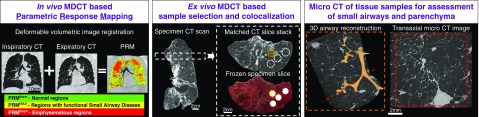
Figure 1.
Overview of image acquisition and tissue processing. Left panel: parametric response mapping (PRM) analysis was performed on in vivo thoracic computed tomography (CT) scans, classifying each voxel of lung into one of three classes: normal (PRMNorm), functional small airways disease (PRMfSAD), and emphysema (PRMEmph). Middle panel: after lungs were removed, each explanted lung specimen was first air inflated and frozen to enable ex vivo scanning with a CT scanner. Subsequently, the lung specimen was cut into 2-cm slices, from which tissue cores were extracted for micro-CT imaging. The micro-CT scans enabled a detailed assessment of small airway morphometry and alveolar destruction. Right panel: finally, sample core locations were matched back to the preoperative in vivo CT scan to enable a correlation between the morphometric parameters and the PRM classification. 3D = three-dimensional; MDCT = multidetector CT.