Figure 32.
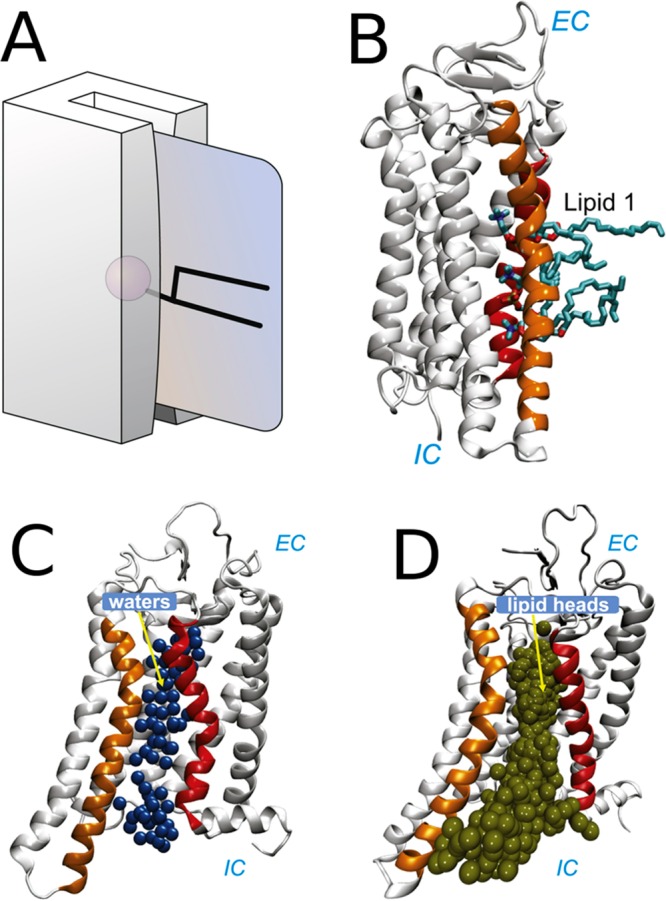
Lipid scramblase function of GPCRs and its mechanism. (A) Schematic representation of the “credit-card mechanism” for lipid flip–flop. Adapted with permission from ref (837). Copyright 2006 Springer Nature. (B) The polar groove formed between the transmembrane helices is filled with water molecules. (C) MD snapshot showing lipids with their headgroups inserted into the groove between two transmembrane helices. (D) Continuous lipid translocation pathway characterized in simulations indicated by overlaid lipid phosphorus atoms. Adapted with permission from ref (847). Copyright 2018 Elsevier.
