Figure 1.
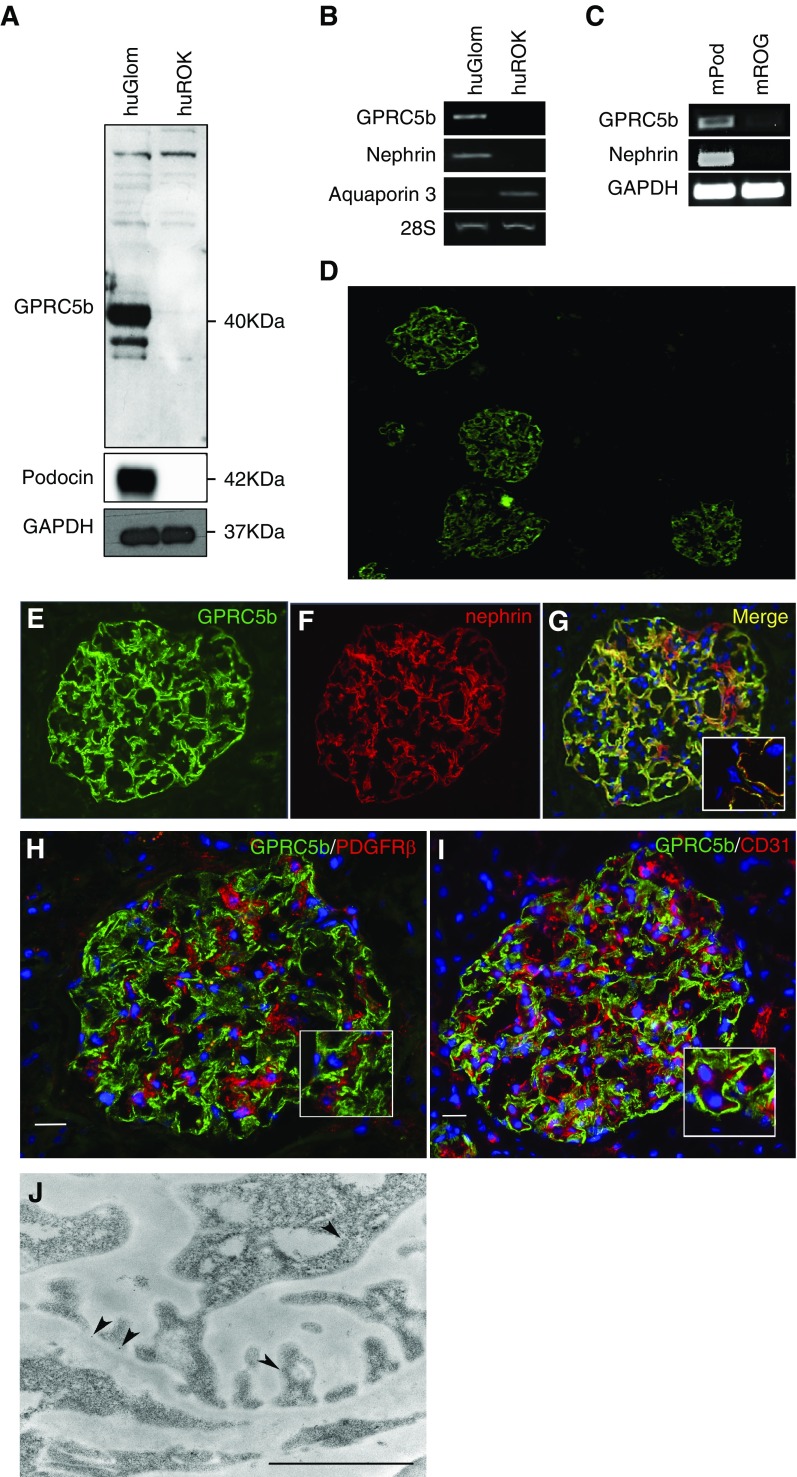
GPRC5b is enriched in human and mouse podocytes. (A) In human kidney, Western blotting for Gprc5b detects a 40 kDa protein only in the glomerulus (huGlom) and not in rest of the kidney (huROK). Podocin was used to show the purity of the glomerular fraction and GAPDH as a loading control. (B) Gprc5b transcript shows strong enrichment in the glomerulus when compared with the rest of the kidney as detected by conventional PCR. Nephrin and aquaporin 3 were used as glomerular and rest of kidney fraction markers, respectively, whereas 28S gene was used as a loading control. (C) The PCR for Gprc5b in FACS-isolated mouse podocytes (mPod) and rest of glomerulus (mROG) shows an enrichment in podocytes. Nephrin was used to validate the purity of podocyte fractions and GAPDH as a loading control. (D) Immunofluorescence staining for GPRC5b (green) in human kidney cortex shows strong immunoreactivity in glomeruli and no significant signal in extraglomerular areas. (E–G) Double staining of Gprc5b (green) and podocyte foot process marker nephrin (red) shows nearly complete colocalization (yellow). DAPI (blue) was used as a nucleus marker. (H and I) Double labeling with the mesangial marker PDGFRβ (red) or with the endothelial marker CD31 (red) does not show significant overlapping reactivity. (J) Immunoelectron microscopy shows gold label for Gprc5b (arrowheads) on podocyte plasma membrane. Magnifications: ×40 in (D), ×200 in (E–G), ×400 in (H and I). Scale bar, 250 nm in (J).