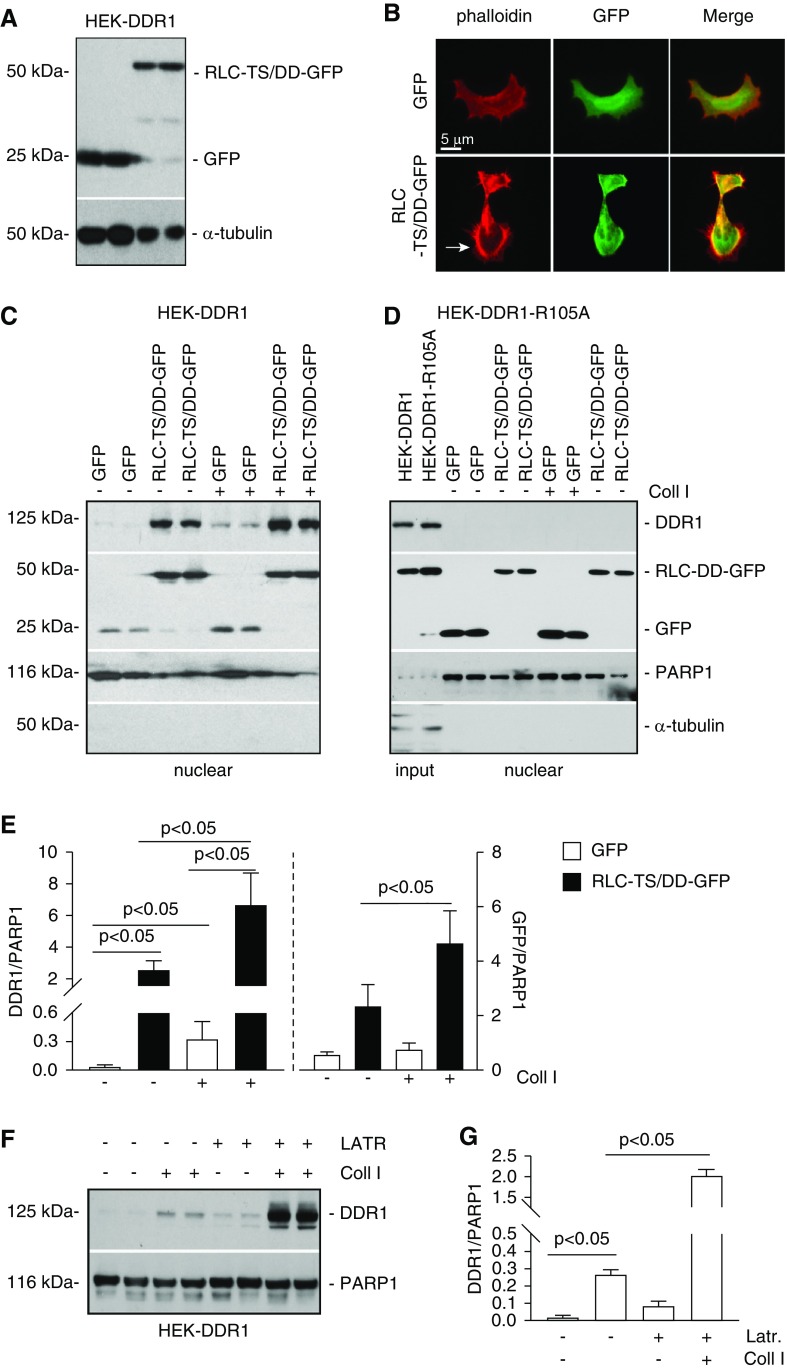
Figure 5.
Nonmuscle myosin II A and β-actin promote DDR1 nuclear translocation. (A) HEK-DDR1 cells were transiently transfected with empty vector (GFP) or constitutively active nonmuscle myosin II RLC (RLC-TS/DD-GFP) cDNA. Cell lysates (20 µg/lane) of cells transfected in duplicate were analyzed by western blot using anti-GFP antibody. α-tubulin was used to verify equal loading. (B) Representative image of HEK-DDR1 cells transfected as indicated above stained with rhodamine phalloidin showing the presence of cortical actin in cells transfected with RLC-TS/DD-GFP cDNA. (C and D) Serum-starved HEK-DDR1 or HEK-DDR1-R105A cells, transfected with GFP or RLC-TS/DD-GFP cDNA, were treated with vehicle or collagen I (50 µg/ml) for 3 hours. Nuclear fractions (20 µg/lane) were analyzed by western blot for levels of DDR1 (with anti-DDR1 antibody) or RLC-TS/DD-GFP and GFP (with anti-GFP antibody). PARP1 and α-tubulin were used to verify equal loading and purity of nuclear fractions. (E) DDR1, RLC-TS/DD-GFP, and PARP1 bands of cells in (B) were quantified by densitometry. Values represent DDR1/or RLC-TS/DD-GFP/PARP1 ratio and are the mean±SD of three experiments. (F) Serum-starved HEK-DDR1 cells were treated with vehicle or collagen I (50 µg/ml) for 3 hours in the presence or absence of Latrunculin B (LATR, 10 µM). Nuclear fractions (20 µg/lane) were analyzed by western blot for levels of DDR1 and PARP1 (used to verify equal loading of nuclear fractions). (G) Nuclear DDR1 and PARP1 bands were quantified by densitometry. Values represent DDR1/PARP1 ratio and are the mean±SD of one experiment performed in triplicate. Coll I, collagen I.