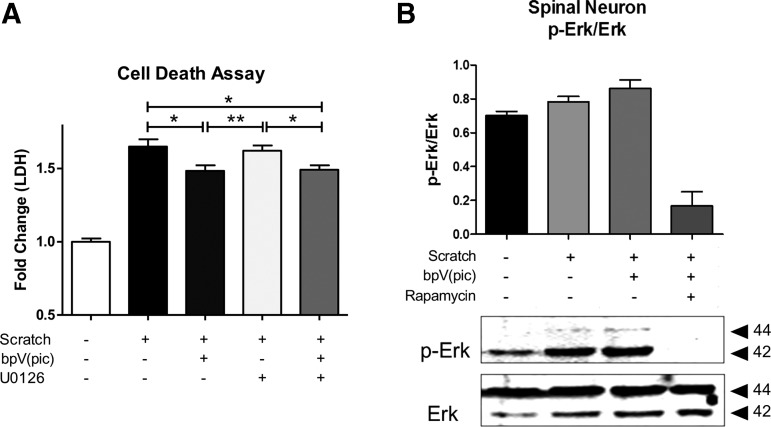
FIG. 4.
Bisperoxovanadium (bpV) promoted extracellular signal-related kinase (Erk) activity in an mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR)-dependent manner. (A) MEK and Erk activity inhibitor, U0126, did not significantly reduce neuron scratch injury-mediated cell death, while bpV did even when combined with U0126. (B) Rapamycin reduced Erk activity, suggesting that the injury induced Erk activation occurred via an mTOR-dependent manner. Data were expressed as mean ± standard error of the mean; n = 3 experiments. All data analyzed via one-way analysis of variance; *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001.