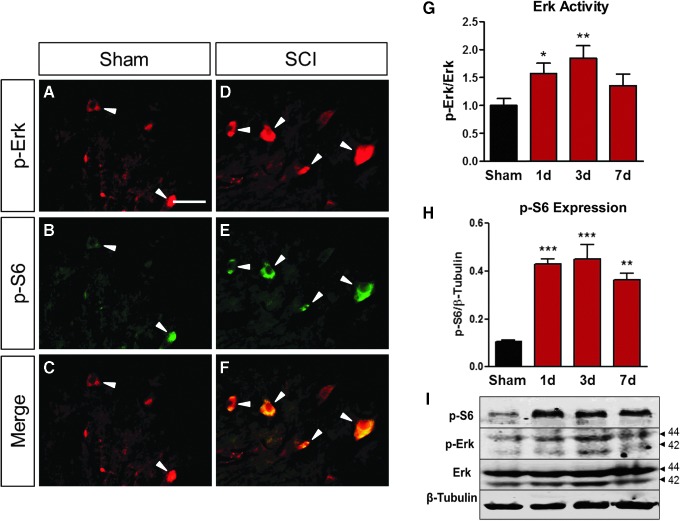
FIG. 7.
Extracellular signal-related kinase (Erk) and p-S6 colocalized and showed similar expression profile in the spinal cord after injury. (A–F) Both p-Erk and p-S6 were highly expressed in the ventral horn motor neurons at 24 h post-SCI compared with the sham control (white arrows). (G,I) The Erk activity and (H,I) p-S6 showed similarly expressional changes over time in the total spinal cord tissue. (I) Representative Western blot images for p-S6, p-Erk, and Erk. β-tubulin served as a loading control. Data were expressed as mean ± standard error of the mean; n = 3 for immunofluorescence double labeling. n = 4–5/time point for Western blot. All data analyzed via one-way analysis of variance; n = 3 for immunofluorescence double labeling. n = 4–5/ time point for Western blot. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001 compared with sham.