Fig. 1.
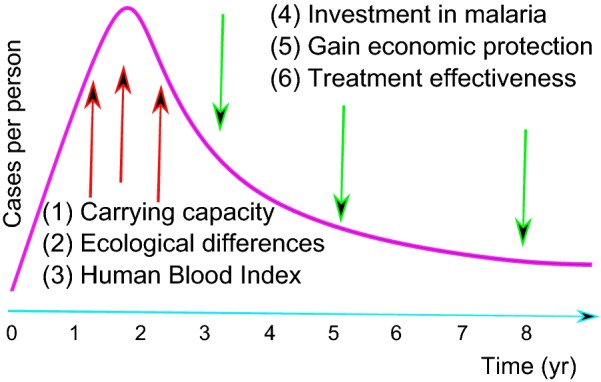
Theoretical background. The convex curve supports the convex trajectory observed in the generalization model [33] of the frontier malaria concept [28]. Environmental conditions (1–3) and socioeconomic factors (4–6) are processes estimated with parameters in the model by Baeza et al. [33]. Environmental conditions (1–3) are driving forces in the high-risk scenario of malaria transmission in the first years of colonization. Socioeconomic factors (4–6) counterbalance and surpass environmental conditions effects, decreasing malaria incidence in the long-term. (1) Carrying capacity: the maximum abundance of adult mosquitoes per unit of land area. (2) Ecological differences: the magnitude of land-use changes. (3) Human Blood Index: the proportion of blood meals from humans by a mosquito. (4) Investment in malaria: the effect of investment in malaria medication. (5) Gain economic protection: the rate which people gain protection against malaria due to the overall economic improvements. (6) Treatment effectiveness: the cost-effectiveness of the treatment
