Fig. 4.
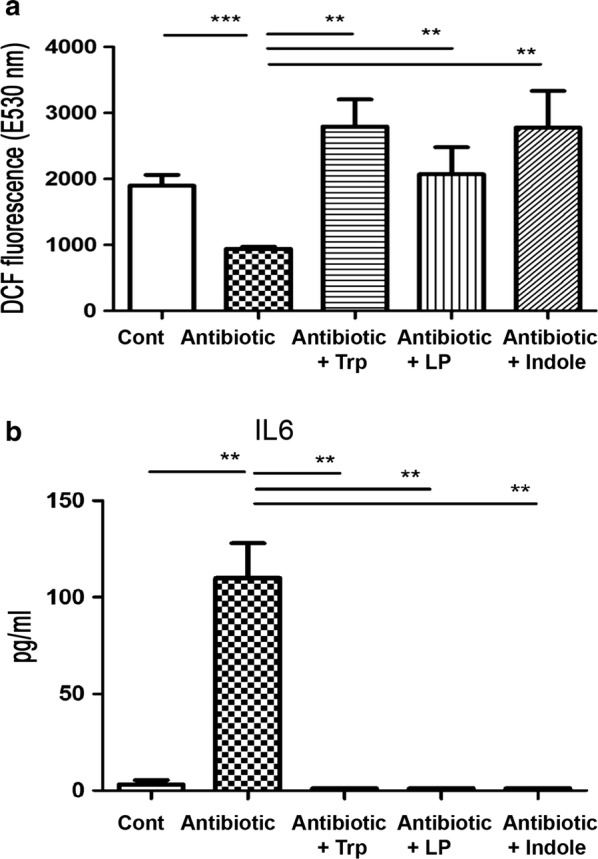
Oral supplementation with Tryptophan, dead L.P., or indole increases ROS levels of the intestinal mucosa and decreases IL-6 levels in the plasma under antibiotic treatment. a Intramuscular combined antibiotic was given to mice for 6 days and ROS production in the intestinal mucosa was examined with the production of DCFDA. The levels of ROS in the intestinal mucosa were analyzed by DCFDA fluorescent dye, which was added into the suspension of intestinal mucosa for the cultivation. DCFDA is oxidized by ROS into 2ʹ7ʹ-dichlorofluorescein (DCF). DCF is detected by fluorescence spectroscopy with excitation and emission spectra of 495 nm and 529 nm, respectively. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. b Antibiotic treatment significantly increased the IL-6 levels in the plasma by 200-fold as compared to that in the control group. Tryptophan or dead L.P. feeding in mice receiving antibiotic treatment decreased the plasma IL-6 levels as compared to those in the antibiotic treatment group. The mouse ELISA kit (eBioscience) was used for IL-6 assay. The blood was centrifuged at 1000×g, 4 °C for 15 min and the serum was collected for use. Data are presented as mean ± SEM; DCF, 2ʹ7ʹ-dichlorofluorescein; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01
