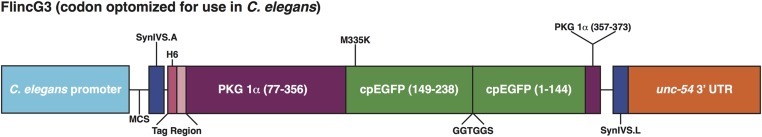
Figure 1.
FlincG3 is a GFP-based cGMP sensor, which has been codon-optimized for use in C. elegans. FlincG3, which was initially characterized as a mammalian cGMP sensor, was codon-optimized for use in C. elegans (figure partially based on Bhargava et al. (2013)). This GFP-based sensor contains two in-tandem protein kinase G (PKG) I α cGMP binding domains that bind cGMP cooperatively (PKG1α (77–356); maroon); this regulatory PKG domain is attached to the N terminus of circularly permuted EGFP (cpEGFP; green). Changing the methionine at position 335, located outside the beta barrel of the cpEGFP domain, to lysine (M335K), improved the response amplitude of the sensor to cGMP (Bhargava et al. 2013). GGTGGS is a linker between the two GFP halves. This linker, along with the 6xHis-tag region (H6) and the Tag Region, were retained from the mammalian FlincG3 sensor. This C. elegans codon-optimized sensor, prepared by Genscript, was inserted into a worm-specific Fire vector, pPD95.75, which contains synthetic introns (SynIVS.A and SynIVS.L; blue) to facilitate expression, a multiple cloning site (MCS) and the 3′ untranslated region of unc-54 (unc-54 3′ UTR; orange).