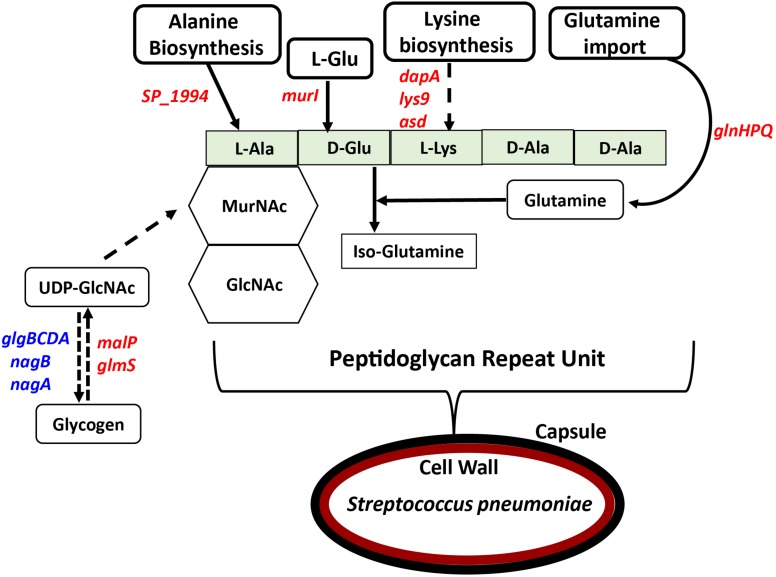
FIGURE 2.
Impact of impaired polyamine synthesis on PG biosynthesis. The PG repeat unit structure in pneumococci constitutes a disaccharide (hexagon) composed of GlcNAc and MurNAc that is linked to an L-Ala, D-Glu, L-Lys, D-Ala, and D-Ala pentapeptide (light green rectangle). RNA-Seq-based comparative transcriptome analysis of ΔcadA impaired in polyamine synthesis and the wild type S. pneumoniae TIGR4 identified gene (italicized) expression changes (increase in blue and decrease in red) that could impact the PG repeat unit synthesis and cross-linking. Enzymatic reactions are shown as black arrows and multi-step reactions are represented by a broken arrow. Reduced synthesis of UDP-GlcNAc due to reduced expression of malP and glmS, and its increased breakdown due to higher expression of nagA, nagB, and the glgBCDA operon, will impact PG synthesis. Reduced expression of SP_1994 that converts pyruvate to alanine, murI that converts L-Glu to D-Glu, and lysine biosynthesis genes (dapA, lys9, and asd) will limit the availability of these three amino acids in PG pentapeptide synthesis. Crosslinking of the PG repeat unit requires conversion of D-Glu to iso-glutamine using glutamine as a co-factor. Impaired glutamine import, due to reduced expression of glnHPQ was observed in ΔcadA. The overall impact of polyamine synthesis impairment is altered cell wall biosynthesis (red oval), due to specific effects on PG synthesis. The cell wall provides the point of structural attachment for the capsule (black oval) in S. pneumoniae.