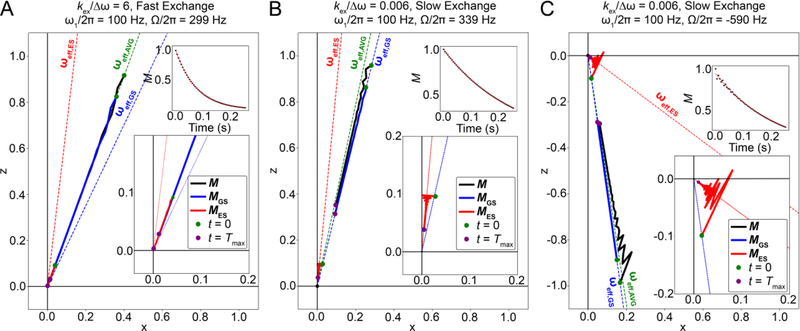
Figure 13.
Time course of the evolution of the normalized GS, ES and net magnetization during an off-resonance R1ρ experiment, simulated using the B-M equations. Time course for the positions of the tips of the GS, ES and net magnetization vectors (each with their base at the origin), denoted as solid blue, red and black lines respectively, with green dots in each case denoting the positions of the vector tips at the start of the relaxation period, and violet dots denoting their positions at the end of the relaxation period, respectively. Directions for the GS,ES and AVG effective fields are denoted using blue, red and green dashed lines, respectively. Also shown as insets are the variations of the normalized projections of the net magnetization along ωeff,OBS (M) as a function of time (black dots), along an exponential fit of the same (red line). Simulations were performed using kex = 20000 s−1 for panel A, kex = 20 s−1 for panels B and C. The other parameters used for all simulations were pES = 0.1, , γ(1H)B0/2π = 700 MHz, R1,GS = R1,ES = 2.5 s−1, R2,GS = R2,ES = 22.5 s−1 and Tmax = 0.25 s. The initial alignment of the magnetization for the B-M and vector simulations was achieved as described in Section 6.1.