Figure 3.
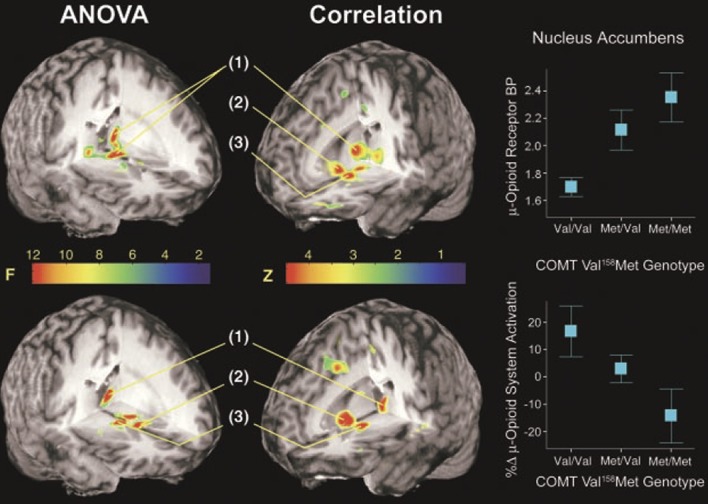
Effects of COMT val158met genotypes and related COMT activity on the mu-opioid system activation induced by sustained pain. Upper left: effects of COMT val158met genotypes on baseline mu-opioid receptor availability. Significant effects on baseline were observed in the anterior and posterior (pulvinar ipsilateral to pain) thalamus (1). Near the multiple comparisons threshold, possible effects were observed bilaterally in the NAc and ventral pallidum and in the contralateral thalamic pulvinar. Lower left: effects of COMT val158met genotypes on the activation of the mu-opioid system during sustained pain stress. Significant effects were observed in the anterior and posterior (pulvinar) thalamus (1) and striatopallidal regions (NAc (2), ventral pallidum (3), and subthalamic nucleus, bilaterally). Upper right: correlations between COMT activity related to the COMT val158met polymorphisms and baseline mu-opioid receptor availability in the NAc COMT activity was coded as follows: −1, met/met; 0, val/met; and 1, val/val. Lower right: correlations between COMT activity and mu-opioid system activation in response to the pain challenge in the NAc.74 From Zubieta JK, Heitzeg MM, Smith YR, Bueller JA, Xu K, Xu Y, Koeppe RA, Stohler CS, Goldman D. COMT val158met genotype affects mu-opioid neurotransmitter responses to a pain stressor. Science 2003;299:1240–3. Reprinted with permission from AAAS. ANOVA, analysis of variance; BP, binding potential; COMT, catechol-O-methyltransferase; NAc, nucleus accumbens.
