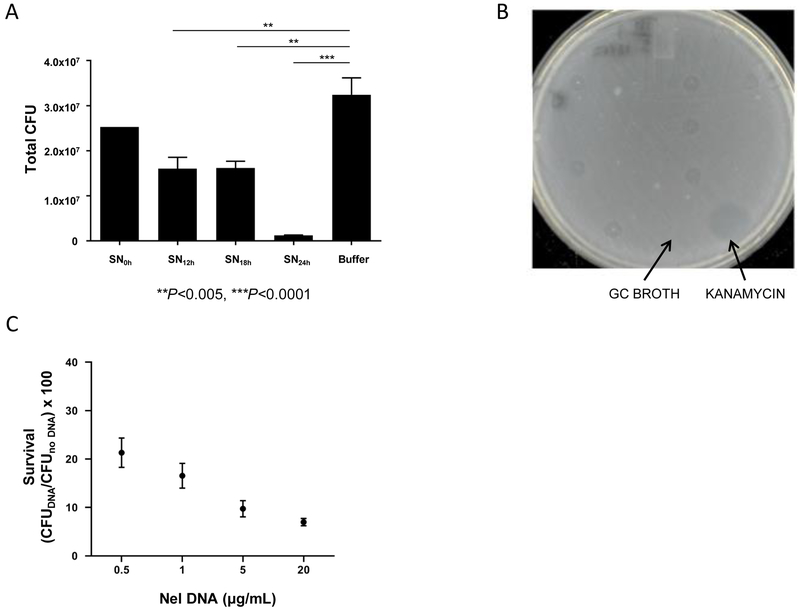
Fig 4. Nel DNA kills Ngo.
(A) Ngo CFUs recovered after a 5 h incubation with cell-free Nel supernates (SN) harvested at the indicated times from liquid cultures. n=3. Error bars: SEM. (**P<0.005, ***P<0.0001; One-way ANOVA with Tukey’s Multiple Comparison Test). Nel DNA concentration in 16, 20, and 24 h SN were 0.31, 0.81, and 2.72 μg/mL, respectively (n=1, see Materials and Methods).
(B) A representative agar plate from a spot assay used to identify the toxic component in cell-free Nel supernates. Undiluted Nel supernates (5 μL each) were spotted onto a lawn of Ngo cells. Clearance, or kill, zones on the lawn after overnight incubation served as the readout for toxicity of the sample for Ngo. Negative control: GC broth. Positive control: Kanamycin (20 μg/mL).
(C) CFUs of Ngo recovered after a 4 h incubation with purified Nel DNA at the indicated final concentrations. Survival is calculated as CFUs of Ngo incubated with DNA normalized to CFUs of Ngo incubated with sterile buffer. Starting Ngo CFU: 5×105. n=4. Error bars represent SEM. LOD: 10 CFUs.