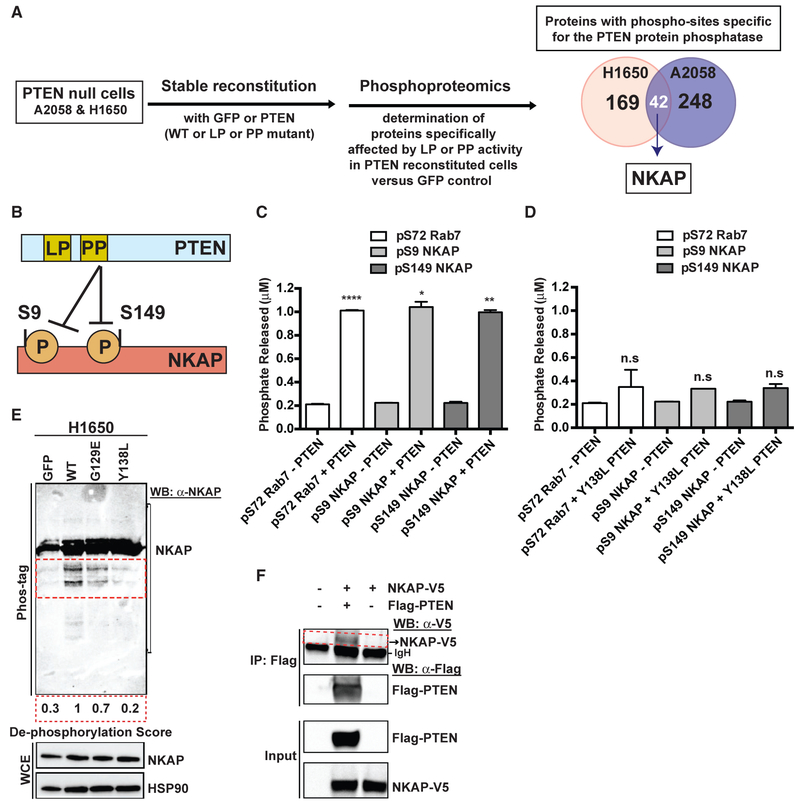
Figure 5. PTEN Dephosphorylates NF-κB-Activating Protein (NKAP).
(A) Left: workflow of the unbiased, global phospho-proteomic profiling in PTEN-deficient cancer cell lines stably expressing PTENWT or PTENG129E or PTENY138L or GFP to identify the phospho-peptides (and corresponding proteins) affected specifically by the protein or lipid phosphatase (PP or LP) activity of PTEN. Right: Venn diagram showing the number of proteins with phospho-sites specifically affected by the protein phosphatase activity of PTEN in H1650 (n = 169) and A2058 (n = 248) cells, with the phospho-proteins (including NF-κB-activating protein, NKAP highlighted in white) affected in both cell lines shown in the overlap (n = 42).
(B) Schematic representation of NKAP phospho-sites at serines 9 and 149 affected by the protein phosphatase activity of PTEN.
(C and D) Phosphate released (μM) from a phospho-S9-NKAP or phospho-S149-NKAP or phospho-S72-Rab7 (control) peptide after incubation without or with recombinant WT PTEN (C) or protein phosphatase mutant Y138L PTEN (D) enzyme in an in vitro malachite green-based colorimetric assay. Data are shown as mean ± SD (n = 2 replicates). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, and ****p < 0.0001 compared with “no PTEN” control by two-tailed unpaired t test with Welch’s correction.
(E) Detection of phospho-NKAP and its de-phosphorylated species (indicated by the red dotted inset) in PTEN-deficient cancer cell lines stably expressing either PTENWT or PTENG129E or PTENY138L or GFP by Phos-tag PAGE and immunoblotting. De-phosphorylation score indicates the extent to which expression of each PTEN mutant in PTEN-deficient cells suppresses NKAP de-phosphorylation relative to PTENWT (set at 1). A lower de-phosphorylation score indicates less de-phosphorylation of NKAP.
(F) Co-immunoprecipitation of NKAP (indicated by the red dotted inset) with PTEN upon overexpression of both NKAP-V5 and FLAG-PTEN and not NKAP-V5 overexpression alone or no overexpression in 293T cells followed by IP-FLAG is shown. Arrowhead denotes NKAP-V5, while the dark band below is background due to secondary antibody cross-reactivity to the immunoglobulin heavy chain (IgH) used in IP.
See also Figure S9.