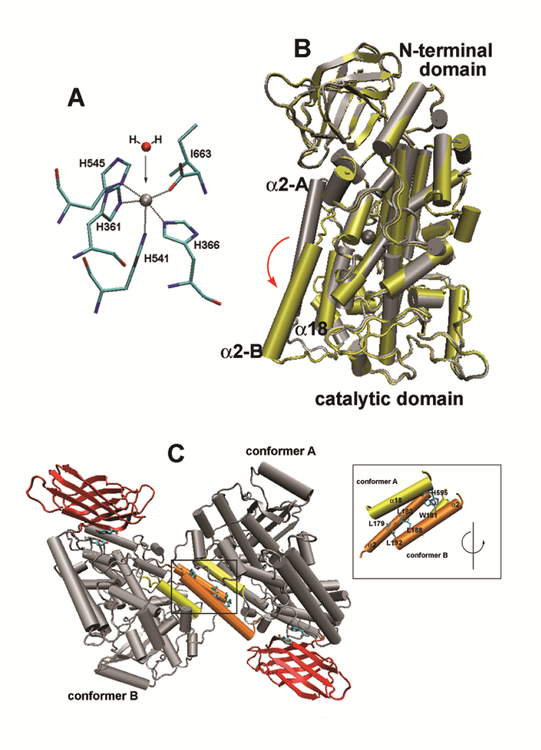
Fig. 7. Structural properties of rabbit ALOX15.
(A) Iron ligand sphere of rabbit ALOX15. Four histidines (His361, His366, His541, His545), the N-terminal Ile/663 and a water molecule are the 1st order iron ligands of rabbit ALOX15 (B). Overlay of the two structures (ligand-free conformer, ligand-bound conformer) of the rabbit ALOX15. Ligand-free conformer A is indicated in grey and ligand-bound structure (conformer B) in yellow. The non-heme iron is also shown. It can be seen that helix 2 is strongly dislocated upon ligand binding by about 12 Å. Rotation of the active site helix 18 can also be seen. (C) Crystal structure of rabbit ALOX15 dimers. In the crystals rabbit ALOX15 forms heterodimers consisting of a ligand-free (conformer A) and a ligand-bound (conformer B) monomer. Inset: The residues contributing to the interaction between the two monomers are indicated and a number of leucine and tryptophane residues contribute. The program VMD 1.4.8 version (University of Illinois) and the coordinates of rabbit LOX complex (PDB code: 2P0M) were used to create these images.