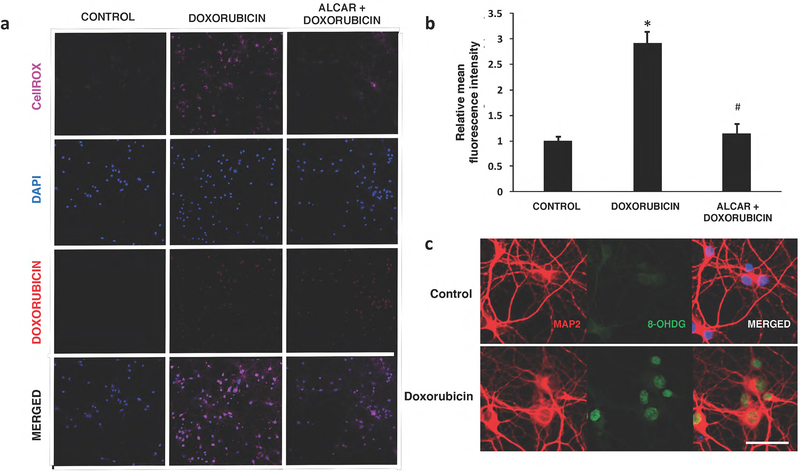
Fig. 7:
Doxorubicin induces oxidative stress in hippocampal neurons. a) An increase in CellROX Deep Red fluorescence was observed in Dox-treated neurons. Doxorubicin autofluorescence in the nucleus was also detected in treated neurons, but not in controls. b) Quantification of signal intensities demonstrate a significant increase in ROS production with Dox. Acetyl-L-carnitine (ALCAR) pre-exposure attenuates levels of ROS in doxorubicin treated cells. Data are shown as mean ± S.E.M. of 10 fields counted in duplicate from three independent experiments. *p<0.05 from control; #p<0.05 from doxorubicin- treated. c) Expression of the DNA oxidative damage marker 8-OHdG in hippocampal neurons.
Representative photos illustrating double immunofluorescence staining of MAP2 (red) and 8 OHdG (green) with DAPI counterstain (blue) in control (top panel) or Dox-treated (lower panel) cells. Strong positive signals for 8-OHdG were predominantly detected in the nucleus of Dox-treated neurons. Scale bar :50 μm