Figure 2:
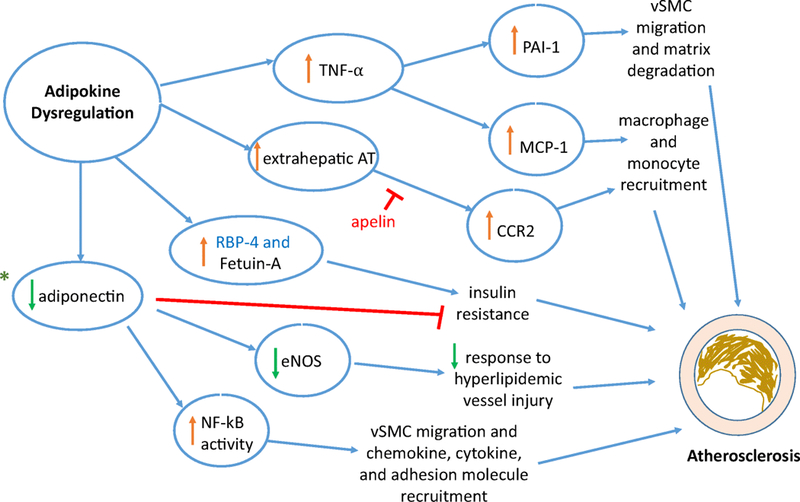
Mediators involved due to adipokine dysregulation leading to the pathophysiology in the development of atherosclerosis.
Adipokines ➔ tumor necrosis factor – alpha (TNF-⍺); extrahepatic angiotensin (AT); retinol-binding protein-4 (RBP-4); fetuin-A, adiponectin, plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (PAI-1); Mediators Impacted ➔ monocyte chemoattractant protein (MCP-1); C-C chemokine receptor type 2 (CCR2) signaling; endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS); nuclear factor-kappa light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells; *Diagnostic targets ➔ genetic predisposition: adiponectin (AdipoQ gene) polymorphisms and specific microRNAs of adipokine dysregulation promoting atherosclerosis; Therapeutic target ➔ apelin; MetS link ➔ RBP-4; vSMC - vascular smooth muscle cells
