Figure 3: Insulin Resistance and Development of Atherosclerosis.
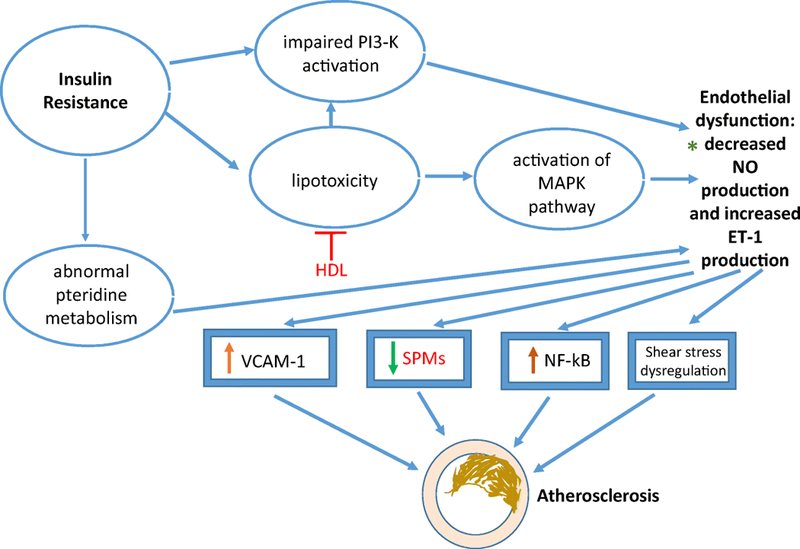
Signaling pathways ➔ phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3-K); mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK); Mediators ➔ nitric oxide (NO); endothelin-1 (ET-1), vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (VCAM-1), nuclear factor-kappa light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells, specialized pro-resolving mediators (SPMs); *Diagnostic targets ➔ genetic predisposition to atherosclerosis: genetic variation in haplotype tagging single nucleotide polymorphisms (htSNPs) at the eNOS locus & specific microRNAs of insulin resistance promoting atherosclerosis; Therapeutic targets ➔ upregulation of high-density lipoprotein (HDL) to induce anti-oxidative effect and reduce lipotoxicity and SPM delivery to resolve inflammation associated with insulin resistance.
