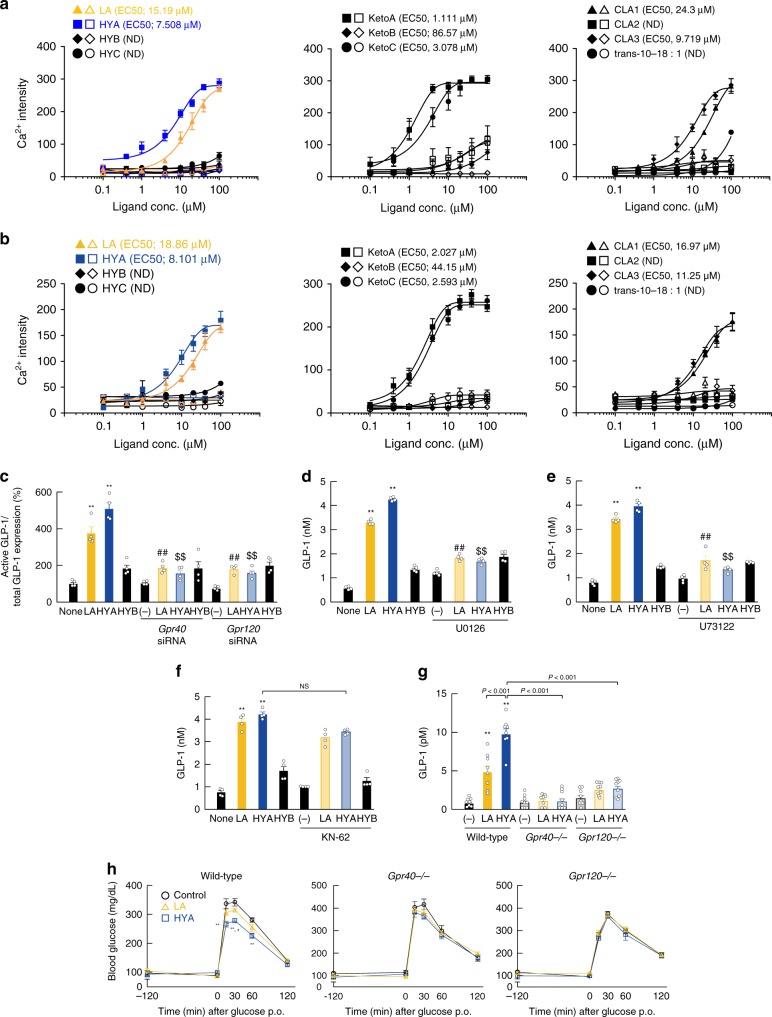
Fig. 6.
HYA contributes to host metabolic condition via GPR40 and GPR120. Mobilization of [Ca2+]i induced by LA-derived gut microbial metabolites was monitored in Flp in a hGPR40 or b hGPR120 T-REx HEK293 cells. Data are presented as Ca2+ intensity. Cells were cultured for 24 h and then treated with or without 10 μg/mL doxycycline (n = 8 independent cultures with doxycycline from three biological replicates; n = 6 independent cultures without doxycycline from two biological replicates). Closed symbols represent values from cells treated with doxycycline, and open symbols denote untreated groups. c–f The inhibitory effects of c Gpr40 and Gpr120 siRNA, d MEK inhibitor (U0126), e PLC inhibitor (U73122), and f CaMKII inhibitor (KN-62) on GLP-1 secretion following LA, HYA, or HYB treatment (n = 4 independent cultures from two biological replicates). **P < 0.01 vs. None (Tukey–Kramer test). ##P < 0.01; #P < 0.05 vs. LA (Tukey–Kramer test). $$P < 0.01 vs. HYA (Tukey–Kramer test). (−) represents untreated cells with siRNA or antagonist. Results are presented as means ± SE. g GLP-1 concentration and h OGTT in wild-type (left, n = 10 animals per group), Gpr40-deficient (middle, n = 8 animals per group), and Gpr120-deficient (right, n = 9, 10, and 9 animals per group) mice were analyzed 2 h after FA administration. **P < 0.01 vs. Control (Tukey–Kramer test). #P < 0.05 vs. LA (Tukey–Kramer test). (−) represents the mice without FA administrations. Results are presented as means ± SE. Source data are provided as a Source Data file 6