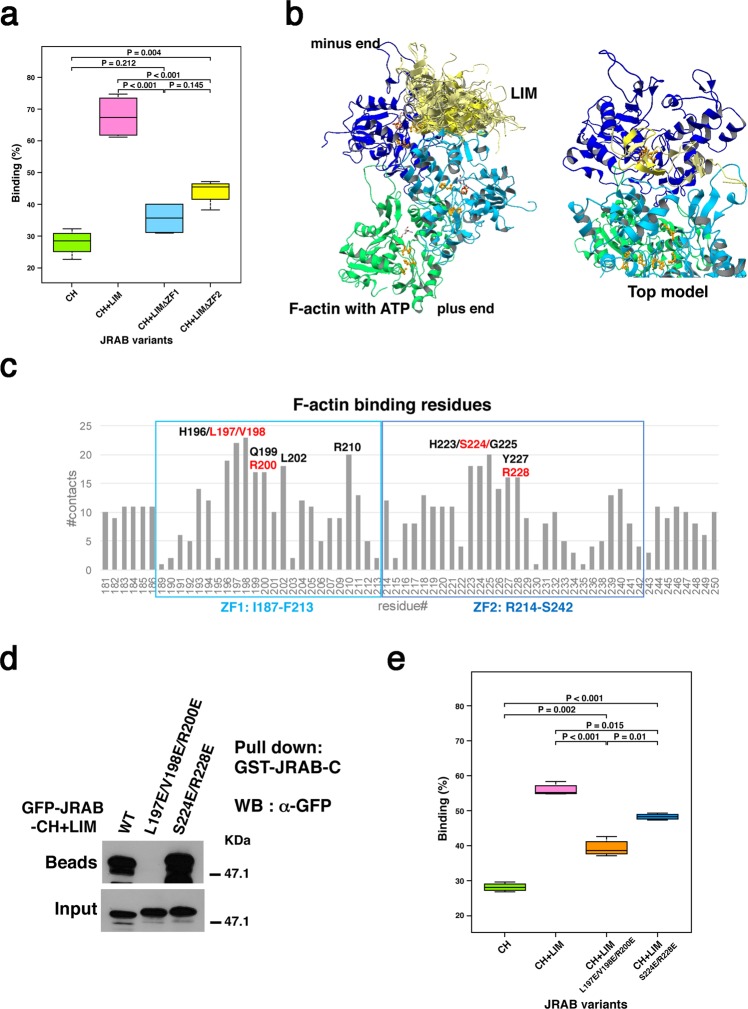
Figure 4.
Three residues of the ZF1 domain are responsible for not only the intramolecular interaction, but also the association of JRAB-LIM with F-actin. (a) F-actin binding assay using the indicated JRAB variants. Graph shows the ratio of each recombinant protein in the pellet vs. total recombinant protein in the pellet and supernatant. Differences among groups were tested by ANOVA with Tukey’s post-hoc multiple comparison test. Differences were considered significant when p < 0.05. See also Supplementary Fig. S2a. (b) Docking simulation between JRAB-LIM and F-actin. The merge of 24 docking models in which LIM binds both the first (blue) and second (cyan) actin monomers from the minus end are shown, along with the top model among them. H73, P109, and H161, which are involved in Pi-release, are colored orange. (c) Numbers of contacts of the residues in JRAB-LIM ZF1 and ZF2 regions with F-actin; the residues that appeared frequently are indicated. The residues colored in red were selected as candidates for the mutation sites to break the interaction with F-actin. To alter the positively charged surface in the putative actin-binding site on LIM to a negatively charged surface, L197, V198, and R200 in the ZF1 region, and S224 and R228 in the ZF2 region were replaced with Glu (E) residues. (d) HEK293 cell lysates containing GFP-JRAB-CH + LIM WT or mutant (L197E/V198E/R200E or S224E/R228E) were subjected to pull-down assays using GST-JRAB-C. The pulled-down protein was detected by WB using anti-GFP antibody. Full-length blot is presented in Supplementary Fig. S7. (e) F-actin binding assay using His-JRAB-CH + LIM mutants (L197E/V198E/R200E and S224E/R228E). Graph shows values as described in (a). Differences among groups were tested by ANOVA with Tukey’s post-hoc multiple comparison test. Differences were considered significant when p < 0.05. See also Supplementary Fig. S2c.