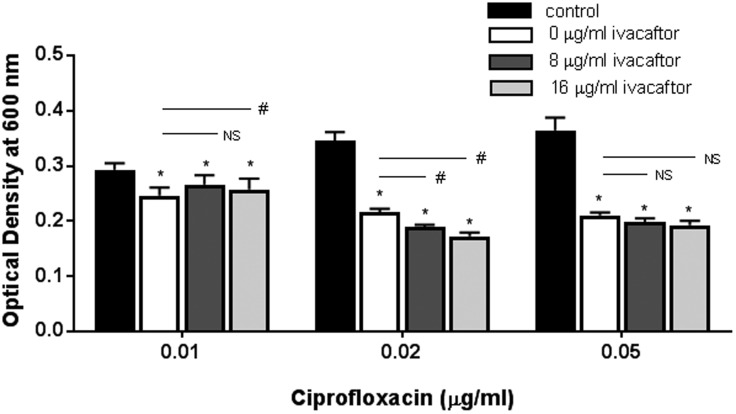
Figure 3.
Enhanced antibacterial activity of ciprofloxacin against Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO-1 in combination with different ivacaftor concentrations. Antibacterial effects of ciprofloxacin and ivacaftor were noticed at the 0.02 µg/mL and 0.05 µg/mL concentrations of ciprofloxacin with 8 and 16 µg/mL of ivacaftor. Two-way ANOVA demonstrated a statistically significant synergism between ciprofloxacin and 16 µg/mL of ivacaftor (P < .0001). Asterisk represents significance of each ciprofloxacin group compared to its respective control group (P < .05, 1-way ANOVA and Tukey’s test). Three different concentrations of ciprofloxacin were used: 0.01, 0.02, and 0.05 µg/mL. Within the same ciprofloxacin group, a statistical difference with P < .05 among different ivacaftor groups was marked by a #. NS means no statistical significance. All groups consisted of at least 4 experiments.