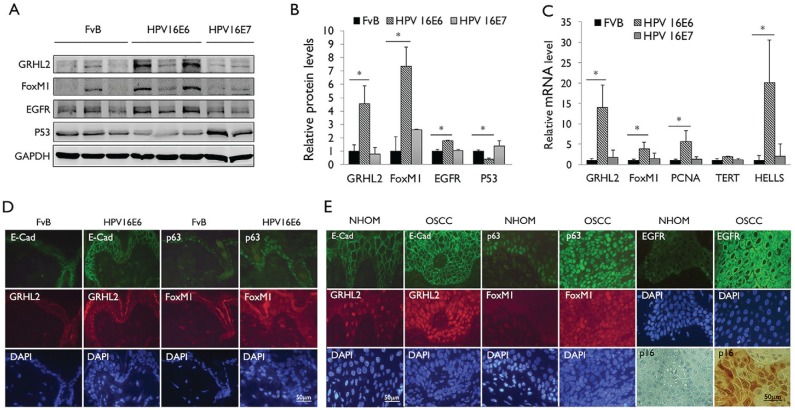
Figure 2.
Human papillomavirus type 16 (HPV-16) E6 induces GRHL2 and FoxM1B expression in epithelial tissue in vivo. (A) Western blotting was performed with epidermal tissues isolated from wild-type mice (FvB) and HPV-16 E6 or HPV-16 E7 transgenic mice for GRHL2, FoxM1B, EGFR, and p53. Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) was used as loading control. (B) Western blotting signals were quantitated by densitometric analysis and plotted with the mean values for wild-type mice (FvB). Bar indicates mean (SD), and * indicates P < 0.05. (C) Quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) was performed with total RNAs isolated from the epidermis of wild-type mice (FvB) and HPV-16 E6 or HPV-16 E7 mice. Experiments were performed in triplicates. Bars indicate standard deviation. * indicates statistically significant change (P < 0.05) compared with wild-type (WT) mice. (D) Skin tissues from HPV-16 E6 transgenic mice were stained for GRHL2, E-cadherin, FoxM1B, and p63 by immunofluorescence staining (IFS). Elevated GRHL2 and FoxM1B were noted in the epidermis of HPV-16 E6 transgenic mice. (E) Immunofluorescence staining was performed with normal human oral mucosa (NHOM) and HPV+ oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) tissues for GRHL2, E-cadherin, p63, and FoxM1B antibody. Numbers of patients with HPV+ OSCC or healthy donors for NHOM were 10. Representative staining results are shown. Nuclei were stained with 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI).