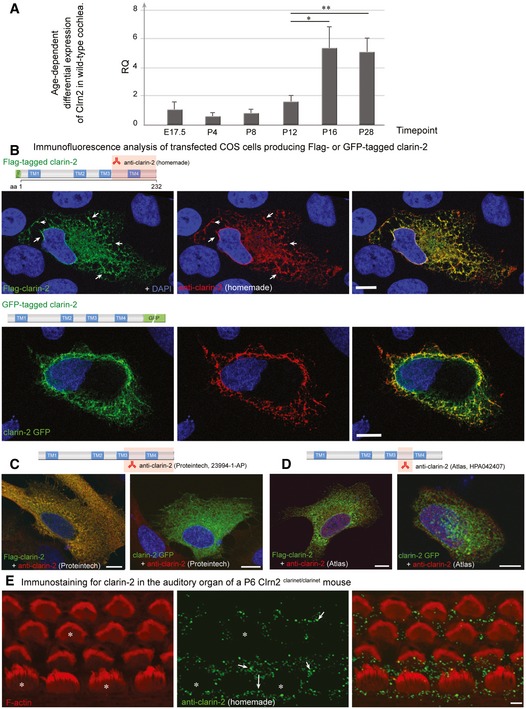
Figure EV4. Age‐dependent differential expression of Clrn2 in wild‐type cochlea, and tests of anti‐Clrn2 antibodies.
-
ART–PCR analysis. To assess the temporal expression of Clrn2 in the cochlea, cochlear RNA was extracted from wild‐type mice at several perinatal and early postnatal timepoints and utilized for qRT–PCR studies to determine the abundance of Clrn2 transcripts. Values were calculated relative to expression level at P4. Expression is constant during embryonic and early postnatal timepoints (E17.5 to P12), then increases ˜3‐fold between P12 and P16. RQ: relative quantification (arbitrary units). For each timepoint, the data shown are mean ± SD of 5 biological replicates. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, one‐way ANOVA.
-
B–DClarin‐2 expression and test of anti‐clarin‐2 antibodies. Transfected HeLa cells producing FLAG‐ or GFP‐tagged clarin‐2 (green) were labelled by the anti‐clarin‐2 antibodies (green): homemade (B), commercial Proteintech (23994‐1‐AP) (C) or Atlas (HPA042407) (D). Only the homemade antibody clearly labelled the two over‐expressed clarin‐2 fusion proteins (overlapping immunostaining in yellow‐some highlighted by arrows, B). Conversely, none of the commercial antibodies could detect the GFP‐tagged clarin‐2, as visualized by the lack of yellow staining in the left panels in (C) (Proteintech) and (D) (Atlas).
-
EImmunostaining using anti‐clarin‐2 homemade antibody showed no specific staining in the F‐actin‐labelled hair cells (asterisks). The white arrows indicate the presence of non‐specific immunostaining over the supporting cells.
