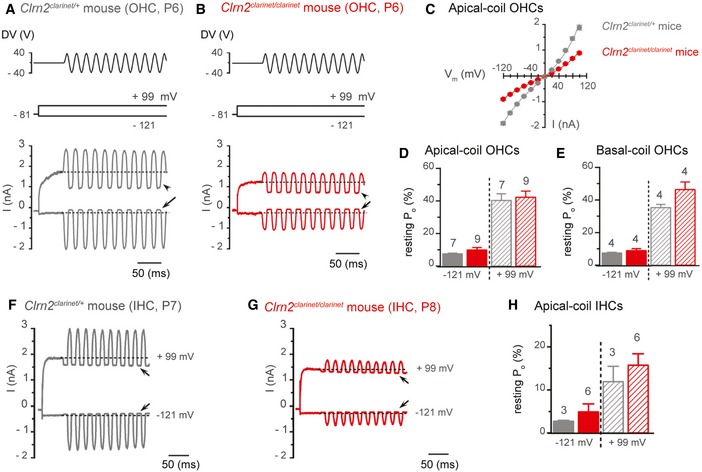
Figure 8. Clrn2 is required for the acquisition of normal mechano‐electrical transducer (MET) function in immature cochlear hair cells.
-
A, BSaturating MET currents recorded from P6 Clrn2 clarinet/+ (A) and Clrn2 clarinet/clarinet (B) apical‐coil OHCs by applying sinusoidal force stimuli of 50 Hz to the hair bundles at −121 mV and +99 mV. The driver voltage (DV) signal of ± 40 V to the fluid jet is shown above the traces (positive deflections of the DV are excitatory). The holding potential was −81 mV. Extracellular Ca2+ concentration was 1.3 mM. Arrows and arrowheads indicate the closure of the MET currents (i.e. resting MET current) elicited during inhibitory bundle displacements at hyperpolarized and depolarized membrane potentials, respectively. Dashed lines indicate the holding current, which is the current at the holding membrane potential.
-
CAverage peak‐to‐peak current–voltage curves recorded from Clrn2 clarinet/+ (grey, P6, n = 7) and Clrn2 clarinet/clarinet (red, P6‐7, n = 9) apical‐coil OHCs.
-
D, EResting open probability (P o) of the MET current at the membrane potential of −121 mV and +99 mV from apical‐ (D) and basal‐coil (E) OHCs. Number of OHCs investigated is shown above the columns. Data shown are mean ± SEM.
-
F, GSaturating MET currents recorded from a P7 Clrn2 clarinet/+ (F) and a P8 Clrn2 clarinet/clarinet (G) apical‐coil IHC using the same experimental protocol described above.
-
HAverage P o of the MET current measured in apical‐coil IHCs at the membrane potential of −121 mV and +99 mV from Clrn2 clarinet/+ (P7, n = 3) and Clrn2 clarinet/clarinet (P7‐8, n = 6) apical‐coil IHCs. Data shown are mean ± SEM.
