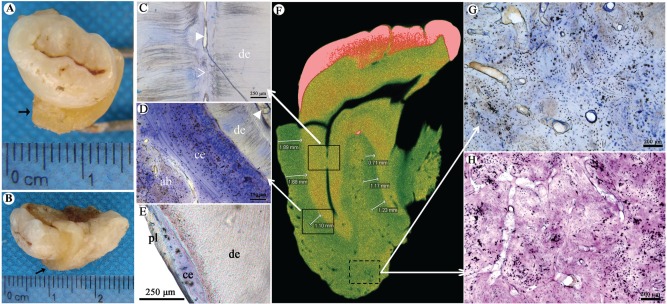
Figure 4.
Abnormal bone and cementum structure. (A, B) The root is surrounded by a thick layer of hard tissue (marked with →). (C–E) Histologic appearance of tooth with toluidine blue staining. Panel C corresponds to the upper solid frame in panel F and shows that the root canal became narrowed and partially sealed with calcified tissues. de, dentin; solid arrowhead, root canal; clear arrowhead, atresia of root canal. Panel D corresponds to the lower solid frame in panel F and shows that the cementum is significantly thickened. There is no clear boundary between cementum and alveolar bone. The thickened cementum is mainly made of cellular cementum. More cementocytes with abnormal cellular process are found. ab, alveolar bone; ce, cementum; solid arrowhead, root canal. (E) Wild-type specimen shows thin cementum and periodontal ligament. pl, periodontal ligament. (F) Micro–computed tomography scanning of the patient’s tooth shows 2 roots of the left maxillary third molar with even and high-density image between the roots and alveolar bone (average thickness, 1.30 ± 0.42 mm). Arrows point to the different insets. (G, H) The changes of alveolar bone roughly corresponding to the dotted frame in panel F. (G) Toluidine blue staining shows disorganized bone structure with irregular medullary cavities scattered in the bone matrix. (H) Hematoxylin and eosin staining shows that structure of the cortical bone is irregularly interrupted by cellular components and matrix with different densities. Osteocytes show the irregularly cellular process.