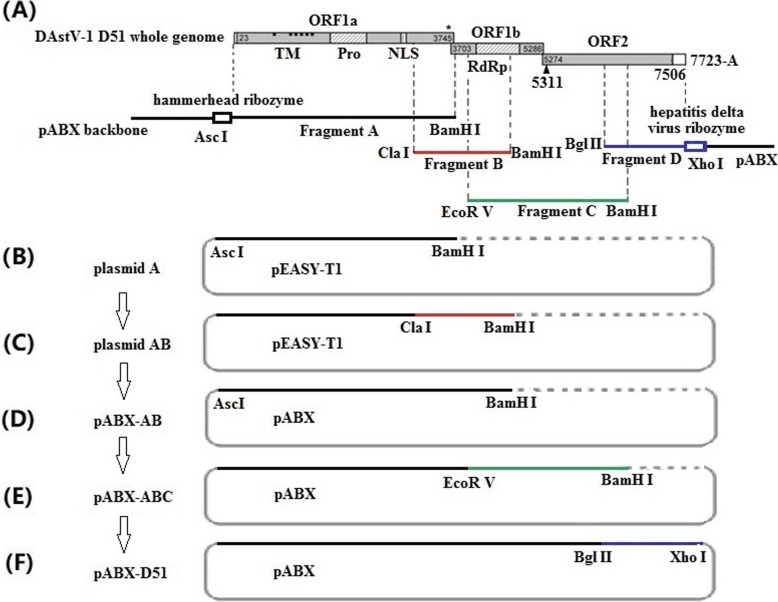
Fig. 1.
Construction of the DNA-launched infectious cDNA clone of the DAstV-1 D51 strain. (a) The organization of the viral genome showing the positions of the unique restriction enzyme site used for cloning. ORF1a, ORF1b and ORF2 indicate the DAstV-1 open reading frames. (b, c, d) Fragments A and B were cloned into pEASY-T1 vector, and then cloned into pABX vector producing pABX-AB. (e) Fragment C was fused into pABX-AB releasing pABX-ABC. (f) Lastly, fragment D was cloned into pABX-ABC obtaining the complete genome of DAstV-1 D51