Fig. 3.
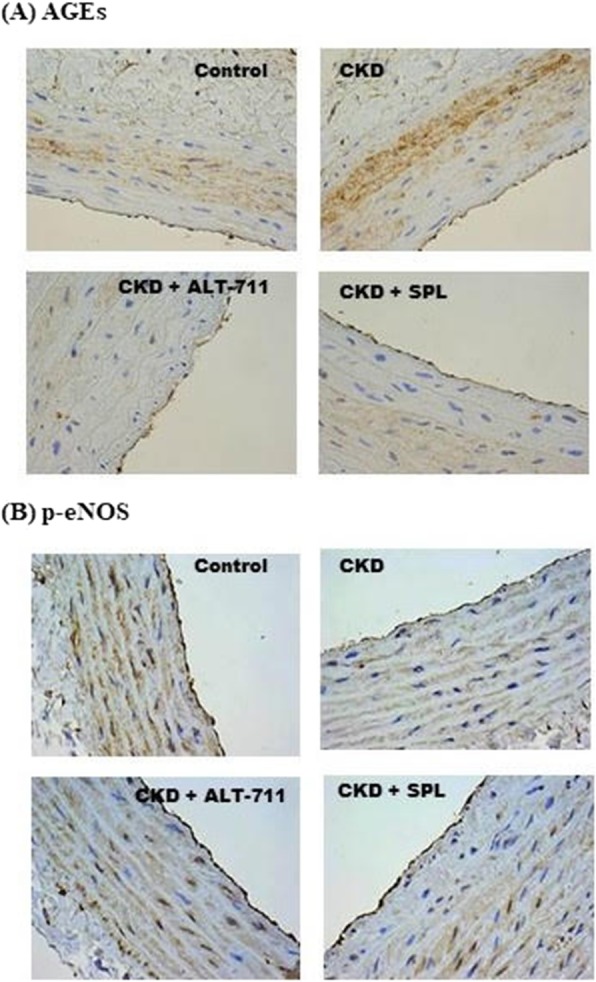
Results derived from the immunohistochemical stain of thoracic aortas obtained from the Sprague-Dawley rats. (a) Accumulation of the advanced glycation end products (AGEs) in thoracic aorta tissue was higher in the chronic kidney disease (CKD) group compared with it was in the control, CKD + ALT-711, and CKD + spironolactone groups. (b) Amount of phospho-endothelial nitric oxide synthase (p-eNOS) in the thoracic aorta tissue was lower in the CKD group compared with it was in the control, CKD + ALT-711, and CKD + Spironolactone groups
