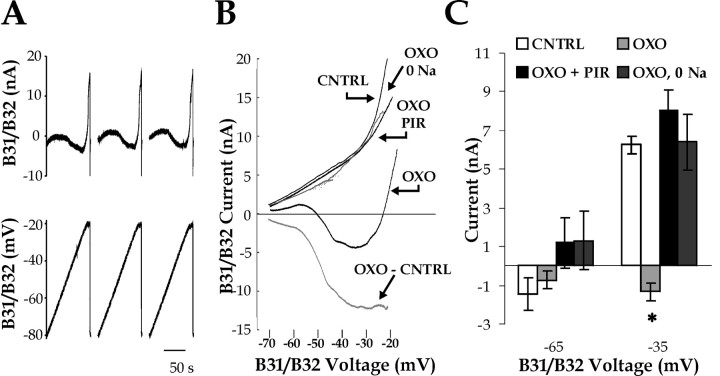
Figure 9.
Oxotremorine (OXO) induces an inward current in voltage-clamped B31/B32. A, Example of the voltage ramps applied to B31/B32 (V) and the resulting current (I), in the presence of OXO. Three consecutive voltage ramps, with a 20 sec delay between them, were applied from –80 to –20 mV at 0.5 mV/sec (see Materials and Methods). B, I--V relationships for several experimental conditions obtained in the same B31/B32. The conditions were tested in the following order: (1) normal ASW with 3.3×10–5 m TTX (CNTRL) (the TTX remained present in each of the subsequent conditions); (2) with the addition of 10–5 m OXO; (3) after substitution of external sodium with NMDG, in the presence of 10–5 m OXO (OXO + 0 Na); (4) after reintroduction of external sodium in the presence of 10–5 m OXO (data not shown, because results were identical to the OXO condition); and (5) with the addition of 10–3 m PIR to 10–5 m OXO (OXO + PIR). In addition, the I–V relationship of the net OXO-induced current (OXO–CNTRL) is plotted in gray.C, Group data. Currents measured from I–V relationships like those in B at –65 mV and –35 mV (CNTRL, n = 8; OXO, n = 9; OXO + 0 Na, n = 3; OXO + PIR, n = 5). The asterisk indicates a statistically significant difference from CNTRL (see Results).