Figure 3.
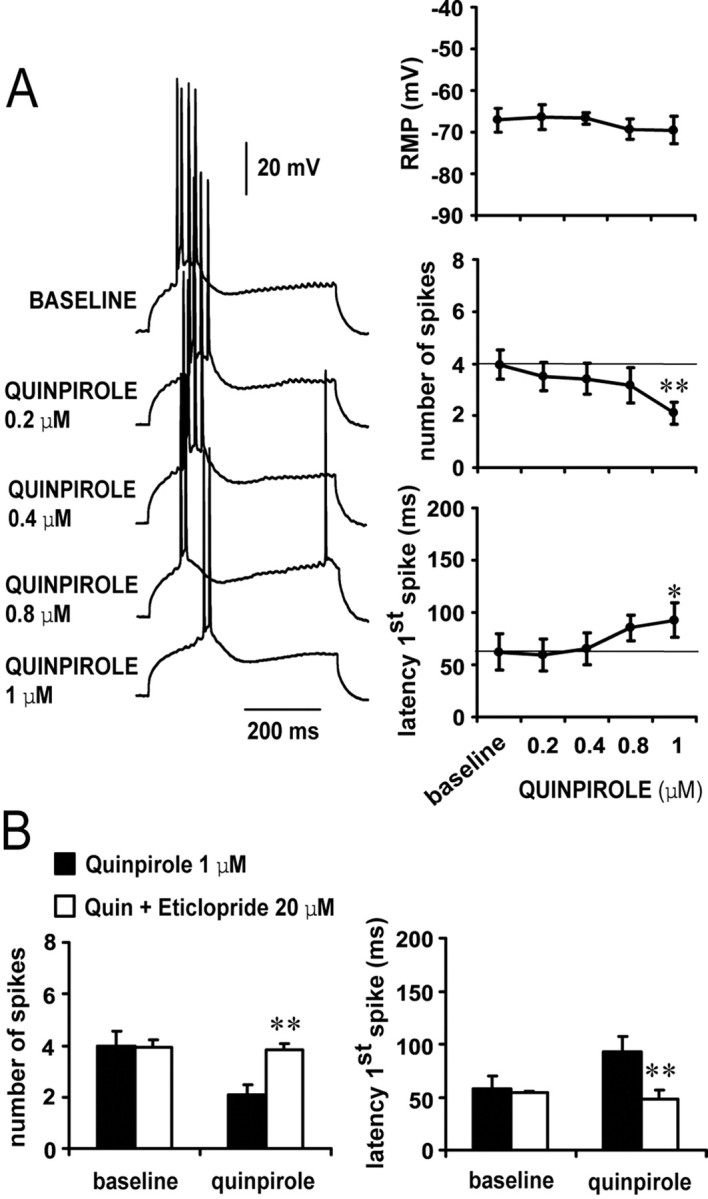
D2 receptors decrease pyramidal cell excitability. A, Concentration-dependent excitability decreases induced by bath application of quinpirole in the PFC. Left panel, Traces recorded from a single neuron illustrating the effects of increasing quinpirole concentrations on action potential firing evoked by depolarizing current injection. Right panel, Dose-dependent effect of quinpirole on PFC pyramidal cell excitability. A significant decrease in the number of evoked spikes and increased first spike latency were observed only with 1 μm quinpirole (compared with baseline; **p < 0.001, *p < 0.01; repeated measured ANOVA). No changes were observed in membrane potential. B, The inhibitory action of 1 μm quinpirole on PFC pyramidal cell excitability was blocked by 20 μm eticlopride (compared with quinpirole alone; **p < 0.001; repeated measures ANOVA).
