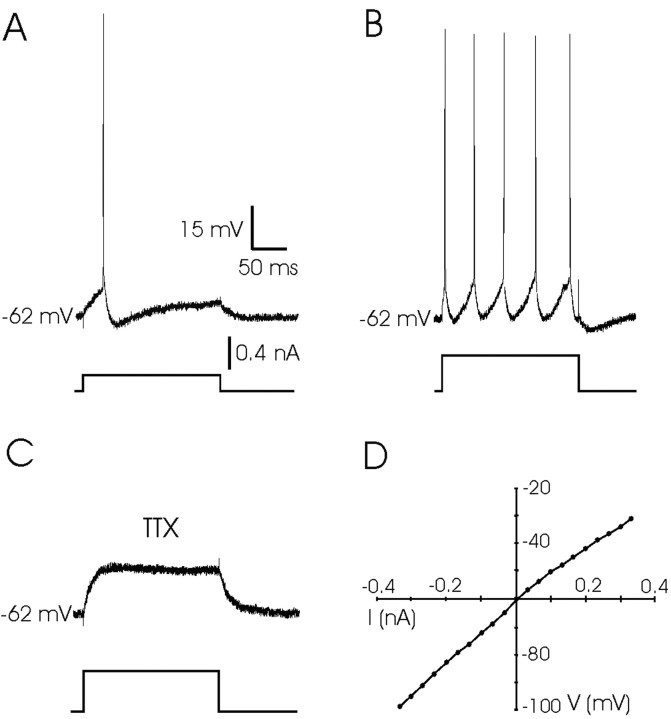
Figure 3.
Response of PH neurons to DC injection. A, A single action potential evoked in a PH neuron with a depolarizing current pulse (0.2 nA, 200 msec). B, A train of action potentials evoked in the same neuron when the current pulse was increased to 0.5 nA. Note the absence of any plateau potential after neuron depolarization by DC injection. C, Example of the response of the same PH neuron after superfusion with TTX (1 μm) in the presence of a depolarizing pulse of 0.4 nA. D, Current–voltage (I–V) relationships for a PH neuron in which voltage-dependent sodium currents were blocked with TTX (1 μm). The resting membrane potential for the neuron was –60 mV. Current pulses were always 200 msec in duration.