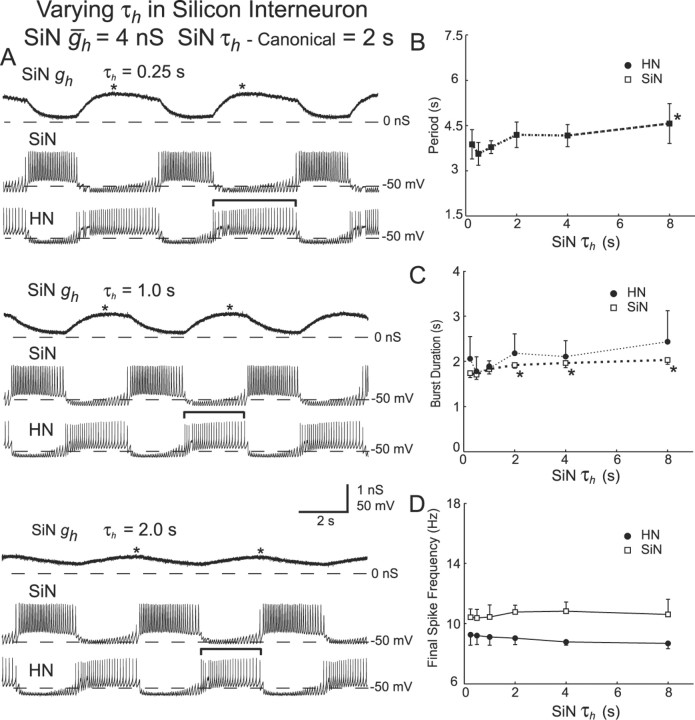
Figure 11.
Variation of τh in the silicon neuron (SiN τh) of a hybrid half-center oscillator. A, Typical activity at three different values of HN ḡh. Voltage traces for the silicon neuron (SiN) and the heart interneuron (HN) and h-current conductance (SiN gh) for the heart interneuron are shown. The burst duration of the unaltered heart interneuron is indicated by brackets. B, Variations in SiN τh have a significant effect on the cycle period. Decreasing SiN τh, down to 0.5 sec, causes a decrease in the cycle period. An additional decrease in SiN τh, however, causes an increase in the cycle period. C, Decreasing SiN τh decreases the burst duration of the heart interneuron and also causes a slight decrease in the burst duration of the silicon neuron. D, Variations in SiN τh have no significant effect on the final spike frequency of either the silicon neuron or the heart interneuron. In B-D, a thick line connecting data points indicates a significant effect of varying SiNτh as determined by ANOVA (p < 0.05), and asterisks indicate a significant difference (p < 0.05) between the measured value and the corresponding value when SiN τh was set at 0.5 sec in pairwise comparisons.